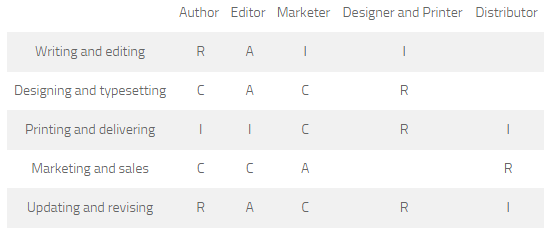
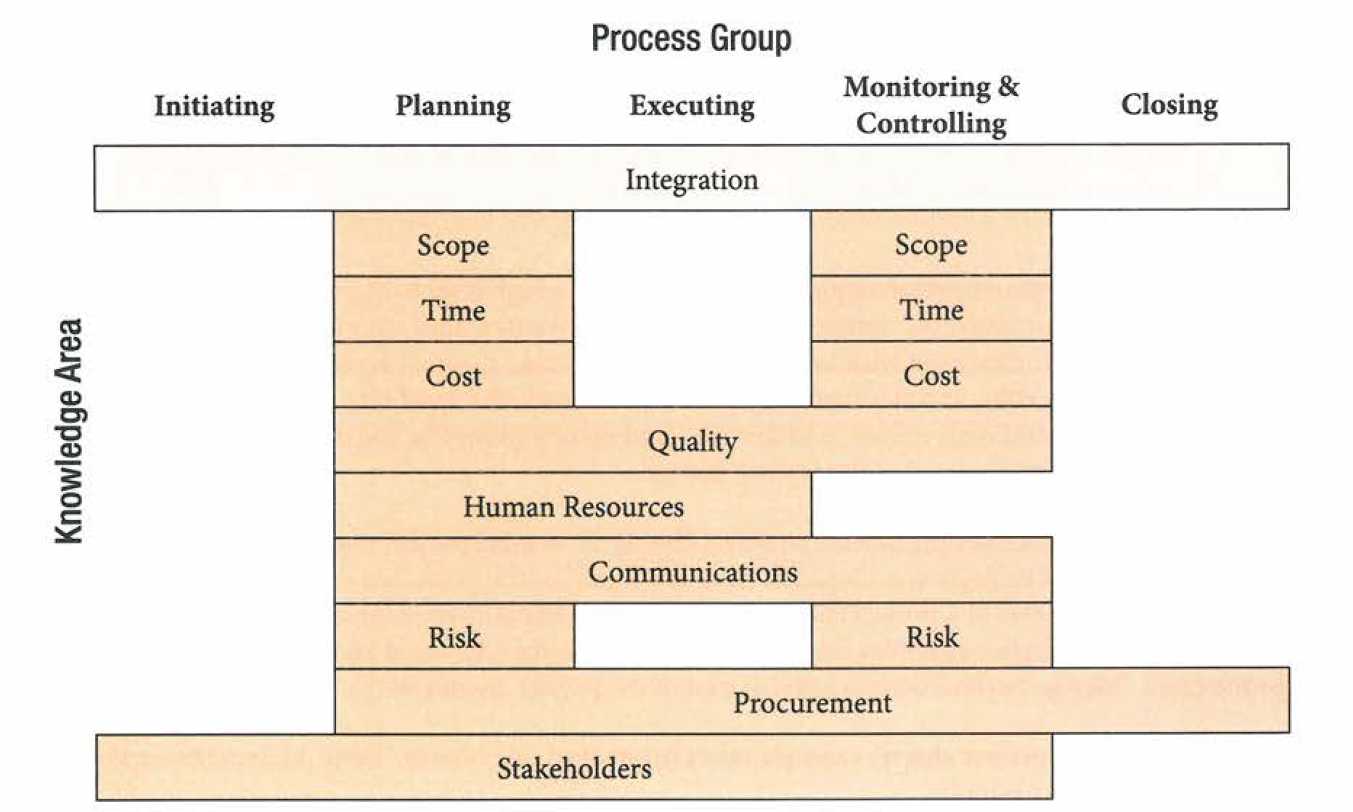
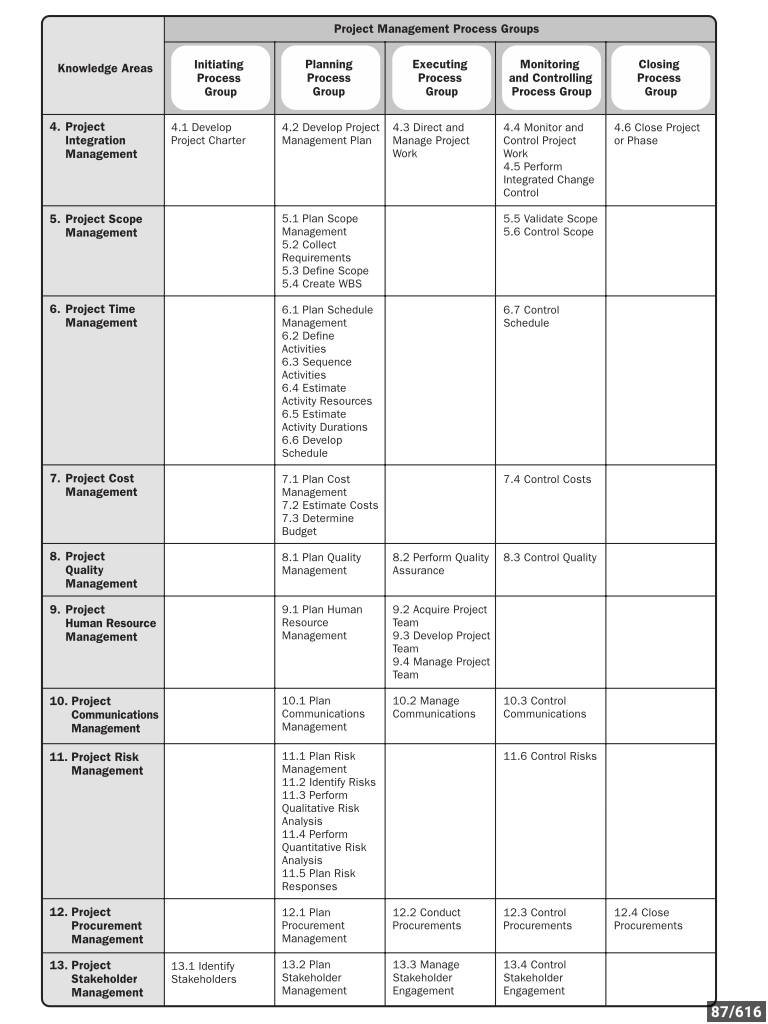
| 31/05/2018 08:37:09~~~~~~manpakhong |
Change Request |
Q: You are a project manager on a data analytics project. When you planned the project, your enterprise environmental factors included a policy which stated that all cost over 5% of the budget should be approved by the VP-Finance. One of your important stakeholders has submitted a change request that would require a 6% increase in the project budget. Your company has an outsourcing effort, and you believe that a small alteration to the way this change is requested could allow you to take advantage of it and reduce your costs by half. What is the best way to handle this type of situation? a. Request approval from the VP-Finance. b. Work with the stakeholder who has requested the change to figure out how to reduce the cost of this change by a third. c. Document the change requested by the stakeholder since all changes must be documented. d. Reject the change as it is over 5% of the budget.
Answer: Request approval from the VP-Finance. Explanation: Refer to PMBOK 6th Edition, Pg 113. You need to follow the company policy and not to find a workaround for the same. Since it is company policy, you will go ahead and ask for approval from the VP-Finance. |
| 28/05/2018 01:03:02~~~~~~manpakhong |
Project Management Plan - Question |
Q: Thomas is a project manager on a construction project. The electrician is already in the process of laying out the wiring, when the customer comes to him with a change request that he needs additional outlets. Thomas thinks that this will increase the cost of the electrical work. What is the first thing Thomas should do? a. Refer to the Project Management plan to see how this change can be handled. b. Refuse to make the change because increasing the cost of the project is making Thomas project over budget. c. Refer to the contract to see if there is any clause like this or not. d. Make the change, since the customer has requested it.
Answer: Refer to the Project Management plan to see how this change can be handled. Refer to PMBOK 6th Edition, Pg 86-88. Remeber if you see the word change or change request, it has to follow the proper change control system. A proper change control procedure is explained in the project management plan. |
| 20/03/2018 02:55:07~~~~~~manpakhong |
Organization process assets |
As per PMBOK the Organizational Process Assets is divided in two categories
1. Processes and procedures The organization's proceses and procedures for performing project work include, but not limited to
2. Corporate knowledge base The PMBOK does not divide the corporate knowledge base according to the process groups. As per the PMBOK the corporate knowledge base includes but not limited to
|
| 20/02/2018 07:43:51~~~~~~manpakhong |
Initializating |
Q: The project charter has been developed for a new medical research project. Who should formally approve this project charter? a. the project team b. the stakeholders c. the project manager d. a member of senior manager
A: a member of senior management
A member of senior management should approve the project charter. The project charter includes the business need for the project. The project charter is created during the Develop Project Charter process and signed by senior management. The project charter is a high-level document that identifies the project manager, the product description, and a description of the business need for the project. It is important that the project charter be approved by someone to whom all team members ultimately report.
|
| 20/02/2018 04:24:17~~~~~~manpakhong |
Risk Management - acceptance |
Q: Developing a contingency allowance to handle a specific risk is an example of which type of risk response? a. avoidance b. mitigation c. acceptance d. transference
Answer: accceptance
Developing a contingency allowance to handle a specific risk is an example of acceptance. Acceptance involves accepting the risk and leaving the project plan unchanged. Examples of acceptance would include taking no action at all or leaving the plan unchanged and developing a contingency or fallback plan. A contingency allowance, or reverve, can be determined by quantifying the impact of the risk. When these reserves are allotted, this would demonstrate acceptance. Developing a contingency allowance is one of the most common ways of accepting a risk. |
| 30/01/2018 06:17:47~~~~~~manpakhong |
Plan Scope Management - Define Scope |
Q: You are in the process of documenting the stakeholder needs and requirements as part of the Collect Requirements process. You need to gather all of the inputs to the Collect Requirements process. Which option is an input to this process? A. enterprise environmental factors B. project charter C. expert judgment D. preliminary scope statement Answer: project charter
In the PMBOK 4th Edition, the inputs to the Collect Requirements process were the project charter and the stakeholder register. In the PMBOK 5th Edition, the inputs to the Collect Requirements are as follows: Scope management plan - an output of the Plan Scope Management process Requirements management plan - an output of the Plan Scope Management process Stakeholder management plan - an output of the Plan Stakeholder Management process Project charter - an output of the Develop Project Charter process Stakeholder register - an output of the Plan Stakeholder Mangement process |
| 29/01/2018 09:05:34~~~~~~manpakhong |
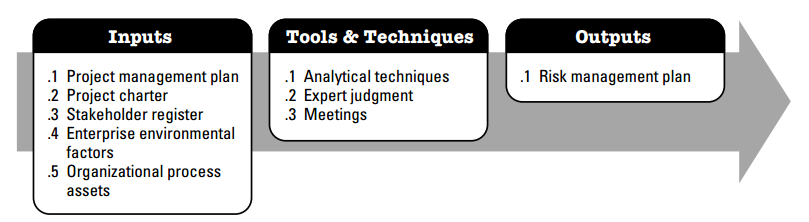
Risk Management - Plan Risk Management |
|
| 29/01/2018 08:02:26~~~~~~manpakhong |
Project Human Resource Management - Conflict Management |
5 general techniques for resolving conflict:
|
| 29/01/2018 07:54:29~~~~~~manpakhong |
Time management - Critical Chain Method |
The critical chain method is another way to develop a bought-into, approved, realistic, and formal schedule. Unlike the other schedule network analysis techniques, it takes into account both activity and resource dependencies. There are many variations of this method, so be careful here. The critical chain method uses a network diagram and critical path to develop a schedule by assigning each activity to occur as late as possible to still meet the end date. You add resource dependencies to the schedule, and then calculate the critical chain. Starting at the end date, you build buffers for resource limitations and risks into the chain at critical milestones (think of this as your time reserves from risk response planning). These reserves, spread throughout the project, provide cushions for delays in the scheduled activities. You manage these buffers so that you meet each individual milestone date and thus the project milestone completion date as well. Note that buffers are not the same as padding. They are planned and inserted to minimize known risks. Do not get carried away with studying this technique; it should not be mentioned on the exam more than three times. And remember, this does not necessarily mean there are three questions about it—it could just be an incorrect choice in a question. |
| 26/01/2018 07:46:37~~~~~~manpakhong |
Risk Management - Acceptance |
Q: Developing a contingency allowance to handle a specific risk is an example of which type of risk response? A. avoidance B. mitigation C. acceptance D. transference Answer: acceptance
Developing a contingency allowance to handle a specific risk is an example of acceptance, Acceptance involves accepting the risk and leving the project plan unchange. Examples of acceptance would include taking no action at all or leaving the plan unchanged and developing a contingency or fallback plan. A contingency allowance, or reserve, can be determined by quantifying the impact of the risk. When these reserves are allotted, This would demonstrate acceptance. Developing a contingency allowance is one of the most common ways of accepting a risk. This would not be an example of avoidance. Avoidance involves modifying the project plan to eliminate the risk or its impact. Examples of avoidance would include limiting the scope of a project or adding resources to a project to eliminate the risk. This would not be an example of mitigation. Mitagation involves reducing the probability or impact of a risk to an acceptable risk threshold. Examples of mitigation would include taking actions to minimize the probability of a risk, performing contigent planning, developing system policies, procedures, responsibilities, and developing planning alternatives. This would not be an example of transference. Transference involves transferring the risk, and its consequences, to a third party. The thrid party is then responsible for owning and managing the risk. One method of transferring risk is to purchase insurance. Many companies self-insure against some risk. Problems that can arise from self-insurance include 1)falling to reserve funds to handle worse case scenarios (low probability events), resulting in severe financial damage to the company, and 2) confusion of business risks with insurable risks. Insurance is one of the most popular ways to deal with risk. |
| 26/01/2018 03:12:24~~~~~~manpakhong |
Cost Management - cost performance without using Earned Value Analysis |
Q: What equation related to cost performance on a project is NOT used in Earned Value Analysis? A. CV = EV - AC B. EV = AC x CPI C. CV = PV - AC D. CPI = EV / AC Answer: CV = PV - AC
The equation CV = PV - AC is not used in Earned Value Analysis
CV or Cost Variance = EV - AC or BCWP - ACWP CPI = EV / AC or BCWP / ACWP EV = CPI x AC |
| 26/01/2018 03:08:50~~~~~~manpakhong |
Net Present Value |
Q: Your company is considering buying a building worth $1 million. If the company buys this building and rents it out for the next five years, it will get $100,000 per year as rent (receivable by the end of each year). At the end of the fifth year, the company will resell the building at $1.1 million. What is the NPV of this investment at 10% per annum discount rate? NPV = discounted inflows - discounted outflows For year 1: PV1 = 100,000 / 1.1^1 = 90,909 For year 2: PV1 = 100,000 / 1.1^2 = 82,645 For year 3: PV1 = 100,000 / 1.1^3 = 75,131 For year 4: PV1 = 100,000 /1.1^4 = 68,301 For year 5: PV1 = 1,200,000 /1.1^5 = 745,106 Hence the total PV of the inflows = 1,062,092 NPV = 1,062,092 - 1,000,000 = $62,092 |
| 24/01/2018 07:03:12~~~~~~manpakhong |
Risk Management |
Q: You have been asked to fill in for another project manager who is on vacation. During the next project status meeting, you ask for a risk report. The project team says that they have never reported on that before and are unsure if there is a master project risk log. What do you do? A. Do nothing B. Develop a list of risks yourself, based on experiences you have had managing similar projects. C. Ask the team to brainstorm the risks they think may impact the project. D. notify the project stakeholders.
Answer: Notify the project stakeholders Report the lack of risk tracking and communication to the project stakeholders. Risk reporting is a key part of any project status meeting. PMI's Code of Ethics and Professional Conduct requires project managers to follow project processes and policies and to provide timely and accurate project information. Failure to track and communiate risks represents a violation of the code. |
| 24/01/2018 04:01:28~~~~~~manpakhong |
Project Quality Management - Inspection vs Prevention |
Q: As a project manager, you are concerned with both prevention and inspection of errors in a work product. The difference between prevention and inspection is: A. Inspection is work done by the Quality Control (QC) team whereas Prevention is work done by the Quality Assurance (QA) team B. Inspection referes to keeping errors out of the process whereas prevention refers to keeping errors out of the hands of the customer. C. Prevention refers to keeping errors out of the process whereas inspection refers to keeping errors out of the hands of the customer. D. Inspection and Prevention refer to the same activity depending on what stage of the project the activity is done.
Answer: Prevention refers to keeping errors out of the process, while inspection referes to keeping errors out of the hands of the customer. The Control Quality process uses a set of operational techniques and tasks to verify that the delivered output will meet the requirements. Quality assurance should be used during the project's planning and executing phases to provide confidence that the stakeholder's requriement will be met and quality control should be used during the project executing and closing phases to formally demonstrate, with reliable data, that the sponsor and/ or customer's acceptance criteria have been met. The project management team may have a working knowldge of sttistical control processses to evaluate data contained in the control quality outputs. Among other subjects, the team may find it useful to know the differences between the following pairs of terms:
|
| 24/01/2018 03:39:22~~~~~~manpakhong |
Project Scope Management - WBS dictionary |
WBS dictionary - The WBS dictionary is a document that provides detailed deliverable, activity, and scheduling information about each component in the WBS. The WBS dictionary is a document that supports the WBS. Information in the WBS dictionary may include, but is not limited to:
|
| 24/01/2018 03:27:35~~~~~~manpakhong |
Cost Management - Funding Limit Reconciliation |
Q: Large variations in the periodic expenditure of funds are undesirable for organizational operations. Therefore, the expenditure of funds is frequently reconciled with the disbursement of funds for the project. According to the PMBOK, this is known as: A. Disbursement reconciliation B. Expenditure Reconciliation C. Budget Reconciliation D. Funding Limit Reconciliation
Answer: Funding Limit Reconciliation This is known as funding limit reconciliation. This will necessitate the scheduling of work to be adjusted to smooth or regulate those expenditures. PMBOK 5th edition p. 212 Funding Limit Reconciliation The expenditure of funds should be reconciled with any funding limits on the commitment of funds for the project. A variance between the funding limits and the planned expenditures will sometimes necessitate the rescheduling of work to level out the rate of expenditures. Thsi is accomplished by placing imposed date constraints for work into the project schedule.
|
| 24/01/2018 03:09:22~~~~~~manpakhong |
Stakeholder Management - Management Skills |
Q: Different stakeholders might require dissimilar overcomes from a project. An integral component of stakeholder management is managing these competing expectations throughout the project from initiation to closure. Which of the following stakeholder management techniques can help in this situation? A. Stakeholder engagment analysis B. Facilitation C. Questionnaires D. Expert judgment Answer: Facilitation The project manager applies management skills to coordinate and harmonize the group toward accomplishing the project objectives. For example:
|
| 24/01/2018 02:52:30~~~~~~manpakhong |
Time Management - Define Activities - Tricks |
We saw the term decomposition used in the Scope Management chapter, in the Create WBS process. Carefully read exam questions using the term. If the team is decomposing work into work packages (deliverables), they are creating a WBS (part of scope management). If they are decomposing work packages into the activities required to produce them, they are in the Define Activities process. |
| 24/01/2018 02:12:22~~~~~~manpakhong |
Time Management - Discretionary dependencies |
Discretionary dependencies - Deiscretionary dependencies are sometimes referred to as preferred logic, preferential logic, or soft logic. Discretionary dependencies are established based on knowledge of best practices within a particular application area or some unusual aspect of the project where a specific sequence is desired, even though there may be other acceptable sequences. Discretionary dependencies should be fully documented since they can create arbitary total float values and can limit later scheduling options. When fast tracking techniques are employed, these discretionary dependencies should be reviewed and considered for modification or removal. The project team determines which dependencies are discretionary during the process of sequencing the activities. |
| 23/01/2018 09:01:31~~~~~~manpakhong |
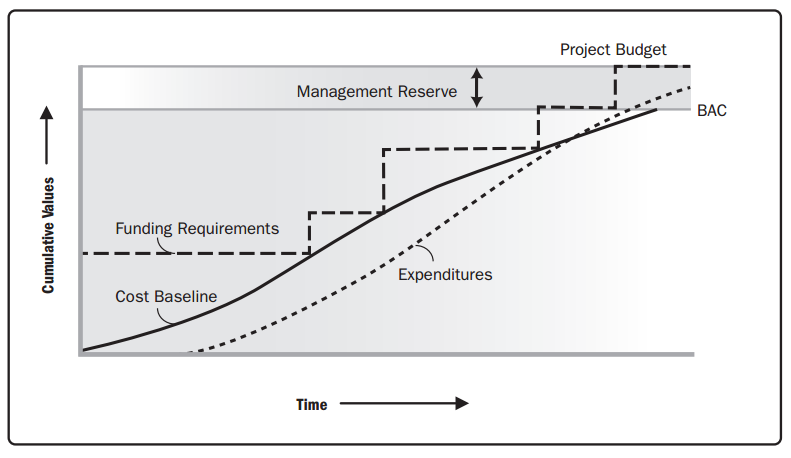
The Cost Performance Baseline |
The cost baseline is the approved version of the time-phased project budget, excluding any management reserves, which can only be changed through formal change control procedures and is used as a basis for comparison to actual results. It is developed as a summation of the approved budgets for the different schedule activities. The summation of the control accounts make up the cost baseline. Since the cost estimates that make up the cost baseline are directly tied to the schedule activities, this enables a time-phased view of the cost baseline, which is typically displayed in the form of an S-curve.
|
| 23/01/2018 07:40:10~~~~~~manpakhong |
Project Quality Management - Process Analysis |
Q: Which of the following Perform Quality Assurance techniques relates to root cause analysis and is used to identify a problem, discover the underlying causes, and develop preventive actions? A. Sensitivity Analysis B. Expected monetary value analysis C. Earned Value Analysis D. Process Analysis Answer: Process Analysis Process analysis follows the steps outlined in the process improvement plan to identify needed improvements. This analysis also exmines problems experienced, constraints experienced, and non-value-added activities identified during process operation. process analysis includes root cause analysis - a specific techinque used to identify a problem, discover the underlying causes that lead to it, and develop preventive actions. |
| 23/01/2018 07:06:30~~~~~~manpakhong |
Estimation methods and their range |
Rough Order of Magnitude estimate = -50% to +50% (PMBOK®) |
| 23/01/2018 02:10:38~~~~~~manpakhong |
Project Integration Management - Configuration Management |
Configuration control is focused on the specification of both the deliverables and the processes; while change control is focused on identifying, documenting, and approving or rejecting changes to the project documents, deliverables, or baselines. Some of the configuration management activities included in the Perform Integrated Change Control process are as follows: Configuration identification - Identification and selection of a configuration item to provide the basis for which the product configuration is defined and verified, products and documents are labeled, changes are managed, and accountability is maintained. Configuration status accounting - Information is recorded and reported as to when appropriate data about the configuration item should be provided. This information includes a listing of approved configuration identification, status of proposed changes to the configuration, and the implementation status of approved changes. Configuration verification and audit - Configuration verification and configuration audits ensure the composition of a project's configuration items is correct and that corresponding changes are registered, assessed, approved, tracked, and correctly implemented. This ensures the functional requirements defined in the configuration documentation have been met. |
| 22/01/2018 09:12:02~~~~~~manpakhong |
Project Integration Management - Configuration status accounting |
Q: One of the configuration management activities in a project involves capturing, storing and reporting configuration information needed to manage products and product information. This is known as: A. Configuration status accounting B. Configuration auditing C. Configuration verification D. Configuration identification
Answer: Configuration status accounting. Information is recorded and reported as to when appropriate data about the configuration item should be provided. This information includes a listing of approved configuration identification, status of proposed changes to the configuration, and the implementation status of approved changes. [PMBOK 5th edition, Pages 195, 198] [Project Integration Management] |
| 22/01/2018 08:49:51~~~~~~manpakhong |
Net Present Value |
Q: Your company is considering buying a building worth $1 million. If the company buys this building and rents it out for the next five years, it will get $100,000 per year as rent (receivable by the end of each year). At the end of the fifth year, the company will resell the building at $1.1 million. What is the NPV of this investment at 10% per annum discount rate?
Hence the total PV of the inflows = 1,062,092
More Example: https://accountingexplained.com/managerial/capital-budgeting/npv |
| 19/01/2018 09:02:06~~~~~~manpakhong |
Procurement - CPIF |
Q: Your company has a fixed price plus incentive fee contract with a vendor. The contract has the following details: Target price: $600,000 Target incentive fee: $100,000 Share ratio: buyer 70% and vendor 30% Actual cost: $650,000 Ceiling price: $725,000 What is the final price your company will have to pay? Step 1: Find the incentive Because the actual cost is greater than the target cost, this indicates a cost overrun. Thus the incentive is negative, as shown below. Incentive = (target cost - actual cost) x vendor's share ratio percentage Incentive = (600,000 - 650,000) x 30 / 100 Incentive = -50,000 x 0.3 = -$15,000 Step 2: Find the overhead fee Overhead fee = target fee + incentive In this case because of the cost overrun, the incentive is negative, so the incentive will be deducted from the vendor's target fee. Overhead fee = 100,000 + (-15,000) Overhead fee = $85,000 Step 3: Find the contract cost Contract cost = actual cost + overhead fee Contract cost = 650,000 + 85,000 Contract cost = $735,000 Step 4: Compare ceiling price with contract cost Ceiling price < contract cost Because the ceiling price is less than the contract cost, the fee paid to the vendor will be limited to the ceiling price, which is $725,000. Had there been no ceiling price, the contract cost would have been $735,000 as computed in Step 3. |
| 19/01/2018 06:49:40~~~~~~manpakhong |
Procurement - Cost Plus Incentive Fee (CPIF) |
Q: You have recently joined an organization as the procurements manager. You have just received an invoice from a contractor. Some of the items from the invoice are as follows: PV of work completed to date: $50,000 AC of work completed to date: $40,000 Total costs reimbursed by the buyer to date: $35,000 If the contract between the buyer and the contractor is a CPIF contract, what is the total value payable to this contractor? (Assume that the contract allows for a 10% fee over actual costs whenever CPI > 1). A. $500 B. $5,500 C. $44,000 D. $55,000 Answer: $5,500
Because the total costs reimbursed released by the buyer to date is $35,000, the actual of work completed to date is $40,000, it has said that the contract allows for 10% fee over the actual costs.
CPI = EV / AC = 50,000 /40,000 = 1.25 Actual cost = 40,000
if (CPI > 1) then 10% fee is applicable on the total cost reimbursable. |
| 19/01/2018 06:49:14~~~~~~manpakhong |
Procurement - Cost Plus Incentive Fee Contract |
Q: Your company (the buyer) has negotiated a cost plus incentive fee contract with a vendor. The contract has a target cost of $300,000. The vendor's target profit is set at 10%, and the share ratio between buyer and vendor is set at 80/20. The actual cost of the contract ends up being $275,000. What is the total cost of the contract to the buyer? Step 1: find the incentive Incentive = (target cost - actual cost) x vendor's share ratio percentage Incentive = (300,000 - 275,000) x 20/100 Incentive = 25,000 x 0.2 = $5,000 Step 2: find the overhead fee Overhead fee = vendor's target profit + incentive Overhead fee = (300,000 x 10%) + 5,000 = 30,000 + 5,000 Overhead fee = $35,000 Step 3: Find the contract cost Contract cost = actual cost + overhead fee Contract cost = 275,000 + 35,000 Contract cost = $310,000 |
| 19/01/2018 06:43:37~~~~~~manpakhong |
Contract cost estimation |
Types of problems to expect (5 types):
Formulas Incentive = (target cost - actual cost) x vendor's share ratio percentage Overhead fee = vendor's target profit + incentive Contract cost = actual cost + overhead fee |
| 11/01/2018 03:57:17~~~~~~manpakhong |
Risk management - tornado diagram |
A tornado diagram is a special type of bar cahrt used in sensitivity analysis for comparing the relative importance of the variables.
|
| 10/01/2018 03:17:28~~~~~~manpakhong |
Deming, Crosby and Juran |
Deming, Shewhart cycle Juran, Pareto Joseph Juran
Crosby |
| 27/12/2017 04:10:25~~~~~~manpakhong |
Project Procurement Management - Supplier agreement |
The common denominator should be a document that is common between the buyer and the supplier, that is the supply agreement. The rest of the choices are the project artifacts what will be different for each party since supplier's scope of work is limited in comparison to the buyer's scope of work. [PMBOK 5th edition, Page 382] [Project Procurement Management]
|
| 27/12/2017 03:04:09~~~~~~manpakhong |
Project Human Resource Management - Resource Histogram |
A chart representing the hours and the time the position, department, or company will be working on the project is an example of a resource histogram. [PMBOK 5th edition, Pages 265, 266] [Project Human Resource Management] |
| 22/12/2017 02:51:23~~~~~~manpakhong |
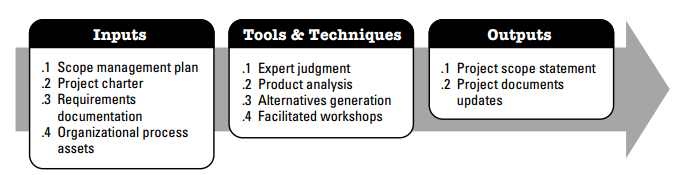
Inputs, Tools & Techniques and Outputs |
|
| 19/12/2017 06:48:57~~~~~~manpakhong | |||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
Quality Management - Tools and Techniques | |||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
|
| 19/12/2017 03:33:23~~~~~~manpakhong |
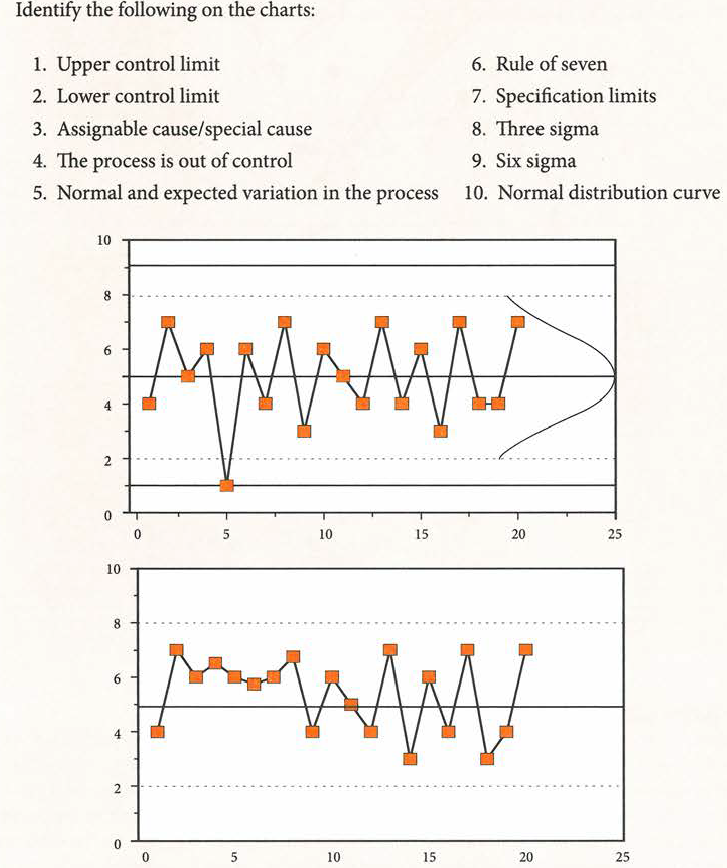
Quality Management - Control Chart |
|
| 23/11/2017 03:35:38~~~~~~manpakhong |
Three-point estimating |
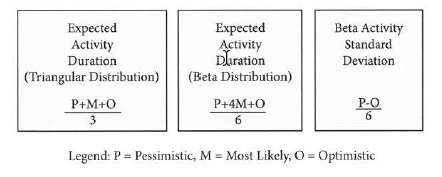
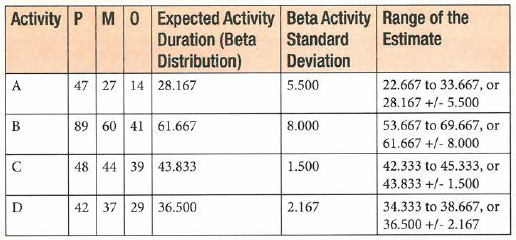
Triangular Distribution (Simple Average) A simple average of the three-point estimates can be done using the formula (P + O + M) /3. The use of simple averaging gives equal weight to each of the three-point estimates when calculating the expected activity duration or cost. Using this formula, the risks (P and O estimates) are considered equally along with the most likely (M) estimate. Beta Distribution (Weighted Average) The use of beta distribution (a weighted average) gives stronger consideration to the most likely estimate. Derived from the Program Evaluation and Review Technique (PERT), this technique uses a formula to create a weighted average for the work to be done. The formula for beta distribution is (P + 4M + O)/ 6. Since the most likely estimate is multiplied by 4, it weights the average toward the most likely estimate. This has the avantage of taking into consideration the benefits of risk management in reducing the uncertainty of estimates. When a good risk management process is followed, the most likely estimates are more likely to occur because risk response plans have been developed to deal with identified opportunities and threats that have been factored into the pessimistic and optimistic estimates.
Range of Estimate = Expected Activity Duration (EAD) - Standard Deviation (SD)
A. B. C. |
| 17/11/2017 09:04:48~~~~~~manpakhong |
Direct costs and variable costs |
Q: A project manager needs to analyze the project costs to find ways to decrease costs. It would be BEST if the project manager looks at: A. Variable costs and fixed costs B. Fixed costs and indirect costs C. Direct costs and variable costs D. Indirect costs and direct costs
Answer: Direct costs and variable costs Direct costs are directly attributable to the project, and variable costs are costs that vary with the amount of work accomplished. It is best to look at decreasing these costs on the project. |
| 17/11/2017 08:38:59~~~~~~manpakhong |
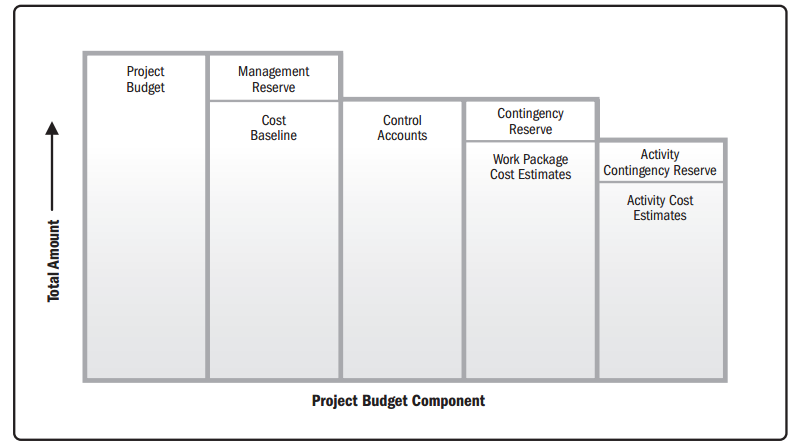
Cost Baseline vs Cost Budget |
Q: The difference between the cost baseline and the cost budget can be BEST described as: A. The management reserves B. The contingency reserves C. The project cost estimate D. The cost account
Answer: Cost accounts are included in the project cost estimate, and the contingency reserves are added to that to come up with the cost baseline. Thereafter, the management reserves are added to come up with the cost budget. The management reserves make up the difference between the cost baseline and the cost budget.
|
| 17/11/2017 07:44:11~~~~~~manpakhong |
Identified risks - Cost Management |
Identified risks are: A. An input to the Estimate Costs process B. An output of the Estimate Costs process C. Not related to the Estimate Costs process D. Both an input to and an output of the Estimate Costs process Identified risks are listed in the risk register, an input to the Estimate Costs process. In completing the Estimate Costs process, additional risks may be uncovered. These are added to the risk register as project documents updates. |
| 17/11/2017 03:43:25~~~~~~manpakhong |
Determine Budget - Cost Management |
Q: The project manager is allocating overall cost estimates to individual activities to establish a baseline for measuring project performance. What process is this? A. Cost Management B. Estimate Costs C. Determine Budget D. Control Costs Answer: Cost Management is too general. The estimates are already created in this situation, so the answer is not Estimate Costs. The answer is not Control Costs, because the baseline has not yet been created. The work described is the Determine Budget process. |
| 17/11/2017 03:35:51~~~~~~manpakhong |
Analogous estimate - Expert Judgment |
Q: Early in the life of your project, you are having a discussion with the sponsor about what estimating techniques should be used. You want a form of expert judgment, but the sponsor argues for analogous estimating. It would be BEST to: A. Agree to analogous estimating, as it is a form of expert judgment B. Suggest life cycle costing as a compromise. C. Determine why the sponsor wants such an accurate estimate D. Try to convince the sponsor to allow expert judgment because it is typically more accurate
Answer: Agree to analogous estimating, as it is a form of expert judgment
This is a tricky question. Determining why the sponsor wants such an accurate estimate sounds like a good idea at first. However, analogous estimates are less accurate than other forms of estimating, as they are prepared with a limited amount of detailed information. Reading every word of this choice helps eliminate it. In order to pick the best answer, you need to realize that analogous estimating is a form of expert judgment. |
| 16/11/2017 08:31:01~~~~~~manpakhong |
Variable costs - Cost Management |
Q: Value analysis is performed to get: A. More value from the cost analysis B. Management to buy into the project C. The team to buy into the project D. A less costly way of doing the same work
Answer: A less costly way of doing the same work Notice that you need to know the definition of value analysis to answer this question. Also notice that the other choices could be considered correct by someone who does not know the definition. Value analysis seeks to decrease cost while maintaining the same scope.
To understand Value Analysis it is necessary to understand some key concepts:
|
| 16/11/2017 04:42:18~~~~~~manpakhong |
Direct Cost, Fixed Cost |
Project setup costs are an example of Fixed costs. Team training is type of Direct cost. You are training the team on skills required for the project. The cost is directly related to the project and thus a direct cost. |
| 16/11/2017 03:10:00~~~~~~manpakhong |
Cost baseline - Cost Management |
Q: A cost baseline is an output of which cost management process? A. Estimate Activity Resources B. Estimate Costs C. Determine Budget D. Control Costs Answer: Determine Budget A cost baseline is an output of the Determine Budget process Plan Cost Management - The process that establishes the policies, procedures, and documentation for planning, managing, expending, and controlling project costs. Estimate Costs - The process of developing an approximation of the monetary resources needed to complete project activities. Determine Budget - The process of aggregating the estimated costs of individual activities or work packages to establish an authorized cost baseline. Control Costs - The process of monitoring the status of the project to update the project costs and managing changes to the cost baseline.
|
| 15/11/2017 08:01:07~~~~~~manpakhong |
Rough order of magnitude estimate - Cost Management |
Q: A rough order of magnitude estimate is made during which project management process group? A. Planning B. Closing C. Executing D. Initiating Answer: Initiating This estimate has a wide range. It is done during project intiating, when very little is known about the project An estimate of costs and time provided in the early stages of a project when its scope and requirements has not been fully defined. An ROM is used to reduce the uncertainty of cost outcomes for both parties when project details have yet to be identified. Rough Order of Magnitude (ROM) Estimates - This type of estimate is usually made during project initiating. A typical range for ROM estimates is -25 to +75 percent from actual, but this range can vary depending on how much is known about the project when creating the estimates. Budget Estimate - This type of estimate is usually made during project planning and is in the range of -10 to +25 percent from actual. Definitive Estimate - As the project progresses, the estimate will become more refined. Some project managers use the range of +/-10 percent from actual, while others use -5 to +10 percent from actual.
|
| 15/11/2017 07:41:58~~~~~~manpakhong |
Parametric estimates - Cost Management |
Q: Which of the following is an example of a parametric estimate? A. Dollars per module B. Learning bend C. Bottom-up D. CPM
Answer: Dollars per module Parametric estimates use a mathematical model to predict project cost or time. |
| 15/11/2017 07:37:02~~~~~~manpakhong |
Life Cycle Costing - Cost Management |
Q: The main focus of life cycle costing is to: A. Estimate installation costs B. Estimate the cost of operations and maintenance C. Consider installation costs when planning the project costs D. Consider operations and maintenance costs in making project decisions.
Answer: Consider operations and maintenance costs in making project decisions. Life cycle costing looks at operations and maintenance costs and balances them with the project costs to try to reduce the cost across the entire life of the project. This concept involves looking at costs over the entire life of the product, not just the cost of the project to create the product. Would it be wise to design the project so that the projects are low but the maintenance costs are higher than the project cost savings? For example, you can plan the project to produce the product at a lower level of quality and save $9,000. After the project is completed, the maintenance costs are $100,000 over the product's life, instead of the $20,000 in maintenance it could have cost had you built the product to a higher quality standard. Your $9,000 project "savings" cost the company $80,000 (or $71,000 in additional cost). This is the concept of life cycle costing - looking at the cost of the whole life of the product, not just the cost of the project. |
| 10/11/2017 07:11:14~~~~~~manpakhong |
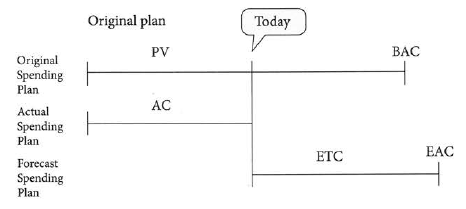
Earned Value Analysis: Forecast - Estimate at Completion |
Estimate at Completion
Estimate at Completion (EAC) is the expected cost of an activity or project at completion. The EAC at any given point in time is calculated using the actual cost of the project thus far and the estimated cost to complete the remaining work. But it can also be calcuated by some other methods depending on the nature of the project. The different ways to determine the Estimate at Completion are as follows: a. Project cost has no deviations from the budget or the rate of spending is the same - Since the amount being spent on the project is in line with established budget, the BAC is used to compute the EAC. EAC = BAC / CPI b. Original estimates are flawed - If original estimates of the cost of the project are flawed, it is best to make a new estimate of the cost of remaining work in order to compute the EAC. This new ETC includes a manual analysis of all the remaining work in the project bearing in mind past performance. EAC = AC + ETC c. Project has atypical variance - Atypical variances imply that the project had an unexpected risk or opportunity that skewed the project performance results. If the risk or opportunity is not likely to be repeated, the variance is considered to be atypical. In this case EAC is EAC = (AC + (BAC - EV))
EAC = AC + [(BAC - EV) / CPI] |
| 10/11/2017 07:10:45~~~~~~manpakhong |
Earned Value Analysis: Forecast - Estimate to Complete |
Earned Value Analysis: Forecast
BAC - Budget at Completion (the budget) - How much did we BUDGET for the TOTAL project effort?
ETC - Estimate to Complete - From this point on, how much MORE do we expect it to cost to finish the project (a forcast)? The method used to calculate the ETC varies depending on the nature of the project estimates and variances
ETC = BAC - EV
ETC = (BAC - EV) / CPI VAC - Variance at Completion - As of today, how much over or under budget do we expect to be at the end of the project?
|
| 10/11/2017 03:19:42~~~~~~manpakhong |
Earned Value Forecast formula |
SPI = EV / PV CPI = EV / AC SV = EV - PV CV = EV - AC Earned Value Forecast formula
Estimate to Completion - ETC = EAC - AC |
| 10/11/2017 03:03:04~~~~~~manpakhong |
Tools and techniques for estimate cost |
a. Bottom-up estimating 1. The Starbuzz across the street opened just a few months ago. Alice sits down with the contractor who did the work there and asks him to help her figure out how much it will cost. He takes a look at the equipment Charles and Jeff want to buy and the specs for the cabinets and seating and tells her what she can afford to do with the budget she has. Tool: Analogous estimating Since Alice is using the contractor's experience with a similar project to figure out how long her project will take, she is assuming that her project will go like the Starbuzz one did. 2. Alice creates a spreadsheet with all of the historical information from similar remodeling projects that have happened on her block. She sits down and types in the guys' desired furnishings and the square footage of the room to generate an estimated cost. Tool: Parametric estimating In this one Alice is just applying some numbers particlar to her project to some historical information she has gathered from other projects and generating an estimate from that.
Tool: Expert judgment Expert judgment offer involves going back to historical information about past projects as well as consulting with experts or using your own expertise. 4. Alice sits down and estimates each and every activity and resource that she is going to need. Then she adds up all of the estimates into "rolled-up" categories. From there she adds up the categories into an overall budget number. Tool: Bottom-up estimating Starting at the lowest level and rolling up estimates is bottom-up estimating. Alice started with the activities on her schedule and rolled them up to categories and finally to a budget number. 5. Jeff sets up an appointment with the same contractor his friend used for some remodelling work. The contractor comes to the house, takes a look at the room, and then gives an estimate for the work. Tool: Expert judgment This is another example of asking somebody who has direct experience with this kind of work to give an estimate. 6. Alice figures out a best-case scenario, a most likely scenario, and a worst-case scenario. Then she used a formula to come up with an expected cost for the project. Tool: Three-point estimates Alice came up with the three estimates and then performed the PERT calculation on them. |
| 09/11/2017 08:16:24~~~~~~manpakhong |
Earned Value Analysis: Forecast - Variance at Completion |
Variance at Completion (VAC) is an indicator of whether the project is over or under the Budget at Completion. It is the difference between the Budget at Completion and the Estimate at Completion. VAC = BAC - EAC if VAC > 0 - the project is under budget if VAC < 0 - the project is over budget if VAC = 0 - the project is on budget |
| 08/11/2017 04:10:38~~~~~~manpakhong |
Change Requests |
Q: To assess the status on your project, you call a meeting of the project team and analyze the project performance based on earned value figures as of today. You find that some of the activities are behind schedule and that the organization is spending more than planned costs on other activities. What would be an output of this meeting? a. rework b. lessons learned c. change requests d. approved corrective actions Answer: change requests
Change requests would be an output of this meeting. Change requests come up after an analysis of project performance, and these requested changes are an output of the Control Communications process. Change requests refer to requests made to change some aspects of the project based on performance evaluation. Requested changes are an input to the Perform Integrated Change Control process. Change requests usually result in changes to the schedule, cost, or scope. All requested changes should be recorded in the change log, even if the change request was denied.
|
| 08/11/2017 03:33:06~~~~~~manpakhong |
Cost Management - Budgeting |
Q: The project team is creating the budget for a new construction project, You need to collect all of the inputs that are needed. All of the following are inputs to this process, EXCEPT: a. cost baseline b. activity cost estimates c. project schedule d. agreements Answer: cost baseline The cost baseline is an output of the Determine Budget process, not an input. In the PMBOK 4th Edition, this output was called cost performance baseline. The determine Budget process involves aggregating the estimated costs of the individual schedule activities or work packages.
|
| 13/10/2017 07:54:25~~~~~~manpakhong |
Cost Management - Accuracy of Estimates |
Rough Order of Magnitude (ROM) Estimates - This type of estimate is usually made during project initiating. A typical range for ROM estimates is -25 to +75 percent from actual, but this range can vary depending on how much is known about the project when creating the estimates. Budget Estimate - This type of estimate is usually made during project planning and is in the range of -10 to +25 percent from actual. Definitive Estimate - As the project progresses, the estimate will become more refined. Some project managers use the range of +/-10 percent from actual, while others use -5 to +10 percent from actual. |
| 10/10/2017 08:51:49~~~~~~manpakhong |
Executing - Manage Communications |
The issue log is not an organizational process assets update. The issue log is considered to be a project document. The inputs to the Manage Communications process are as follows:
The tools and techniques used by the Manage Communications process are as follows:
The outputs of the Manage Communications process are as follows:
The Manage Communications process is part of the Project Communications Management Knowledge Area and Executing Process Group. The Project Communications Management Knowledge Area was changed significantly in the PMBOK 5th Edition and now consists of the following three processes:
The key benefit of the Manage Communications process is that it enables efficient and effective |
| 10/10/2017 07:47:15~~~~~~manpakhong |
Independent Estimates |
Independent Estimates The buyer may compare the seller’s proposed cost with an estimate created in-house or with outside assistance. This allows the buyer to discover significant differences between what the buyer and seller intend in the procurement statement of work. The buyer must have their own estimates to check reasonableness and cannot rely solely on the seller’s cost estimates. An independent estimate can help you figure out why the pricing in a seller's proposal might be very different from what you anticipated. An independent estimate, which can be done internally or externally, is an assessment of the work that will be contracted out to sellers. An independent estimate is also known as a "should-cost" estimate. |
| 06/09/2017 08:39:36~~~~~~manpakhong | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
Cost Management - formulas | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
Benefit-cost ratio Cost-benefit ratio = cost / benefit (if > 1, the project is a profitable venture)
Opportunity cost Sunk cost Depreciation STRAIGHT-LINE DEPRECIATION Straight-line depreciation = cost of the asset / life of the asset
ACCELERATED DEPRECIATION - Declining Balance Method
- Sum of the years method
Break-even analysis Return on sales Return on Assets Return on assets = (net income before or after taxes / total asset value) * 100 Return on Investment Working Capital Ratio Working capital = current assets - current liabilties |
| 04/09/2017 22:31:16~~~~~~manpakhong |
Cost Management - Accuracy of Estimates |
Organizations often have different standards for different ranges of accuracy of estimates: preliminary -> conceptual -> feasibility -> order of magnitude -> definitive estimate Standards:
|
| 03/09/2017 23:04:40~~~~~~manpakhong |
Analogous Estimating vs Parametric Estimating |
Planning, in particular project cost and time planning, requires a lot of estimation as the work involved has not happened yet. In real-world project management and the PMP® Exam, estimation usually involves two distinct types of methods: Analogous Estimating and Parametric Estimating. This post will expound on the similarities and differences of the two kinds of estimation methods. Analogous Estimating vs Parametric Estimating
Though both Analogous Estimating vs Parametric Estimating are based on the historical information from the organization/industry to estimate cost/duration for the project/activity, there are some very noted differences between them:
In addition to the two types of estimation methods detailed above, the PMBOK® Guide has also mentioned two other estimation methods:
Illustrated ExampleFor the exam prep project, before the actual preparation, Aspirants are highly advised to make a project plan for their exam studies by detailing the scope and estimated timeframe. There are 10 Knowledge Areas identified in the PMBOK® Guide. Suppose it is known that it would take 10 hours for going through 1 project management Knowledge Area, the time taken to go through all the 10 Knowledge Areas would be:
Parametric Estimating is employed here since we have the data to know the “unit duration” for the exam project (but beware that the length and difficulty of each individual Knowledge Area for the PMP® Exam is different from the others, the actual time spent on each Knowledge Area would be quite different in my experience). Suppose you have taken the CAPM® Certification Exam in the past with a total of 300 hours of preparation. And since the CAPM® and PMP® Certification Exams are both offered by PMI, you try to make use of Analogous Estimating here to estimate it would take 300 hours for the exam preparation.
|
| 03/09/2017 21:40:41~~~~~~manpakhong |
Project Procurement Management - Aribitration |
Q: You are building a mile-long bridge on a T&M contract. During the excavation activity you found out that some telephone cables are crossing the alignment where you have to construct the bridge. You need to relocate these telephone cables but there is no provision of such an activity in the contract. Further, the relocation of the cables will be a costly task and a lot of government paperwork needs to be done as well. You requested an amendment in the contract but the buyer has rejected it. Despite many efforts you both have not been able to resolve this issue. What should you do next? A. Terminate the contract following the termination procedures mentioned in the contract B. File a judicial petition in accordance with the state's law C. Seek arbitration following the ADR procedures in the contract D. Relocate the cables at your own expense since the activity is not covered by the contract Answer: Seek arbitration following the ADR procedures in the contract In this scenario there has been an increase in the scope of works. Since the contract doesn't accommodate this, the contractor rightfully requested for an amendment. However, since both parties cannot settle this amicably, the next step is to seek aribitration. [PMBOK 5th edition, Page 384] |
| 29/08/2017 08:23:43~~~~~~manpakhong |
Project Cost Management - Cost Management Plan |
Q: The Cost Management Plan is an output of the Plan Cost Management process. This plan is then integrated with other project plans in which of these processes? A. Develop Project Management Plan Answer:
|
| 16/08/2017 07:04:53~~~~~~manpakhong |
Project Stakeholder Management - Communications management |
Q: What is the document for the Project's escalation process? A: Communications management plan Communications management plan vs Stakeholder management plan Although there is a lot of overlap of information between the project communication management and stakeholder management plans, the project escalation process is only documented in the communications management plan. [PMBOK 5th edition, Pages 206, 403] [Project Stakeholder Management] |
| 16/08/2017 06:59:25~~~~~~manpakhong |
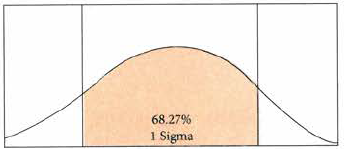
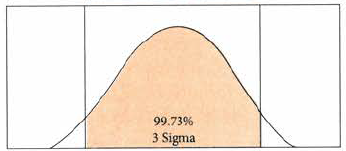
Project Quality management - +/1 3sigma |
The upper/ lower control limits are normally set at + / - 3 sigma. |
| 16/08/2017 06:51:11~~~~~~manpakhong |
Project Time Management - milestone list |
A milestone list is a valid output of the Define Activity process. |
| 16/08/2017 04:43:44~~~~~~manpakhong |
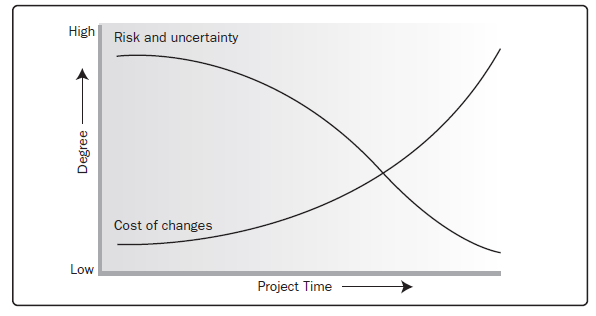
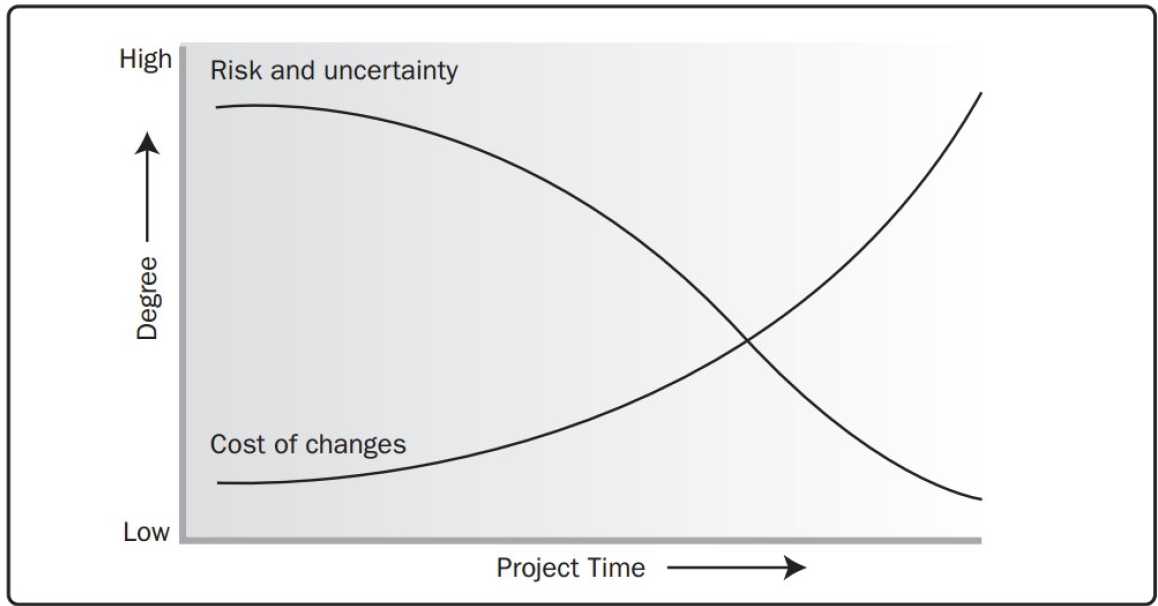
Project Stakeholder Management - Adaptive Project Life Cycles |
While these characteristics remain present to some extent in almost all project life cycles, they are not always present to the same degree. Adaptive life cycles, in particular, are developed with the intent of keeping stakeholder influences higher and the costs of changes lower throughout the life cycle than in predictive life cycles.
|
| 02/08/2017 03:19:37~~~~~~manpakhong |
Project Quality Management |
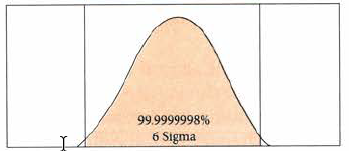
Quality is defined as the degree to which the project fulfills requirements. 3 or 6 Sigma (Note that Six Sigma” is a methodology for organizational process improvement and achieving high levels of correctness with extremely reduced variances.) At 6 sigma, less than 1.5 out of 1 million doors produced will have a problem. At 3 sigma, approximately 2,700 will have a problem. Achieving 6 sigma requires extensive planning. In some organizations, 3 sigma might be acceptable because the amount of planning you’d have to do to reach 6 sigma would be cost- and time-prohibitive. A project under 3 sigma requirements is going to allow a wider range of variance, and planning and control will not require such attention to detail.
|
| 26/07/2017 03:54:29~~~~~~manpakhong |
Project Procurement Management |
Q: Work Performance Data is an important input to the Control Procurements process. Which of the following is not a component of Work Performance Data? A. Data regarding supplier's conformance to quality standards Answer: Data on status of deliverables progress is part of Work Performance Information and not Work Performance Data. The subtle difference between Work Performance Information confuses many people, however it is very important to clearly distinguish between these two concepts.
Work Performance Information
Three inputs to Work performance data:
Work Performance data --> Work Performance Measurements Work Performance Data, Information and Reports - The PMBOK' Guide uses three different terms—work performance data, work performance information, and work performance reports—to differentiate the various stages of project data and information. Work performance data are the initial measurements and details gathered during project work (executing). When work performance data have been analyzed for conformance to plan during controlling processes, they become work performance information. This information can then be organized into work performance reports, which are distributed to the various stakeholders who need to receive and possibly act on the information. |
| 25/07/2017 04:16:04~~~~~~manpakhong |
Project Scope Management- Product acceptance criteria |
The project scope statement documents and addresses the characteristics and boundaries of the project and its associated products and services, as well as product acceptance criteria and scope control. |
| 25/07/2017 04:12:18~~~~~~manpakhong |
Project Stakeholder Management - Phase 1 to Phase 2 |
Q: Linda is a project manager in charge of an online banking project. The project has completed phase 1 and is moving into the next phase of the project. For phase 2, which of the following processes must be performed first? A. Define Scope
Linda needs to initiate the second phase of her project. There is no need to revisit the Develop Project Charter process. However, she needs to revisit the Identify Stakeholders process to determine any change in the stakeholders for the second phase of the project. Stakeholder identification is a continuous process. [PMBOK 5th edition, Page 31] |
| 25/07/2017 03:42:46~~~~~~manpakhong |
Project Communications Management |
Efficient communication means providing only the information that is needed; nothing more, nothing less. [PMBOK 5th edition, Page 290] [Project Communications Management] |
| 24/07/2017 04:21:28~~~~~~manpakhong |
Project Communications Management |
Lucy is managing a high-tech software development project. She has been lucky in acquiring the best performing employees of the organization. However, the project team is not communicating effectively causing delays. The project communications plan is in place but it seems like it is not being followed. The communication plan outlays the communications requirements but does not explicitly assign responsibilities. What should Lucy do first? (assume that all of the following actions need to be taken at some stage) A. Persuade the team to follow the plan Answer:
|
| 22/07/2017 19:10:06~~~~~~manpakhong |
Project Scope Management |
The WBS represents all product and project work. The total work at the lowest levels should roll up to the higher levels s that nothing is left out and no extra work is performed. This principle is also called the: A. 100% rule Answer The WBS represents all product and project work. The total work at the lowest levels should roll up to the higher levels so that nothing is omitted and no extra work is performed. This primciple is also called the 100% rule. [PMBOK 5th edition, Page 131] |
| 21/07/2017 08:15:22~~~~~~manpakhong |
Project Cost Management - Estimate to Complete (ETC) |
Estimate to Complete (ETC) = BAC (Budget At Completion) - EV (Earned Value) Q: A project was estimated to cost $200,000 with a timeline of 10 months. Due to a shipment delay, the schedule was slightly delayed. However, this was made up by shipping the first batch of materials for the project by air. The net result was that there was some additional cost in the project. At the end of the second month, the Project Manager reviews the project and finds that the project is 20% complete and Actual Costs are $50,000. The Estimate to Complete (ETC) for the project would now be:
|
| 21/07/2017 07:44:06~~~~~~manpakhong |
Project Integration Management |
Q: The Banks in Ukraine have raised the annual interest rates sharply to 30%. You have the option to invest your money either in Ukrainian banks or to build a small factory for a client. The total cost of building the factory will be $12 million but will be spread evenly over one year ($1 million payable by the end of each month for the next 12 months). The client will make a payment of $3.9 million at the end of each quarter from the start of the project. Which of the following is the best option (if you are only considering the return on investment)?
|
| 21/07/2017 07:09:29~~~~~~manpakhong |
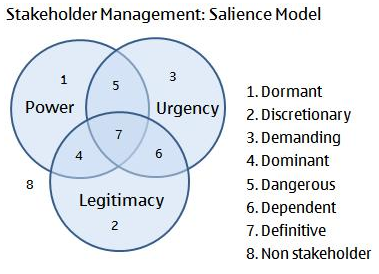
Project Stakeholder Management - Classification Models |
Stakeholder analysis generally follows the steps described below:
There are multiple classification models used for stakeholders analysis, such as:
|
| 21/07/2017 06:44:01~~~~~~manpakhong |
Project Integration Management - Benefit-to-cost ratio (BCR) |
Q: Nancy is carrying out cost-benefit analysis for a project. If undertaken, the project will start in January next year and end by December. The project will incur a constant cost of $10,000 each month (payable by the end of each month) giving a total cost of $120,000 for the project. The revenue from the project will be collected on a quarterly basis. The toal revenue for the project by the end of December will be $20,000. The opportunity cost of the project is 12% which is the bank interest rate Nancy can get if she does not invest in this project. The total present value of all cash outflows is $112,551, while the total present value of all cash inflow is $185,721. What is the benefit-to-cost ratio for the project? Benefit-to-cost ratio (BCR) = PV of inflows/ PV of outflows = 1.65 The gross BCR can also be calculated as Total Revenue/ Total Cost. However, since the total present value of both the inflow and outflow is given, this must be used for a more accurate calculation. $10,000 - constant cost (payable by the end of each month)
|
| 21/07/2017 04:03:18~~~~~~manpakhong |
Project Quality Management - Flow Chart |
|
| 21/07/2017 01:27:06~~~~~~manpakhong |
Project Time Management - Rolling Wave Planning |
In Rolling Wave Planning, the work to be accomplished in the near term is estimated in detail at a low level of the Work Breakdown Structure (WBS), while the work far in the future is estimated as WBS components that are at a relatively high level of the WBS. The work to be performed within another one or two reporting periods in the near future is planned in detail during the current period. |
| 21/07/2017 01:16:20~~~~~~manpakhong |
Quality Management - Conformance Cost vs non-Conformance Cost |
Cost of Conformance vs Cost of Non-Conformance
Both the Cost of Conformance and the Cost of Non-Conformance can be collectively referred to as the Cost of Quality. Cost of Conformance is considered much lower than the Cost of Non-Conformance. Therefore in the PMP® Exam, quality management advocates “prevention over inspection”. Q: All of the following are examples of the cost of nonconformance EXCEPT: Answer: As a project manager of a project, you are analyzing the costs which have been incurred. Which of the following costs cannot be classified under cost of non-conformance? A. Quality Assurance Costs Answer: The Quality Assurance Costs are part of the cost of conformance.
|
| 21/07/2017 01:02:02~~~~~~manpakhong |
Project Scope Management |
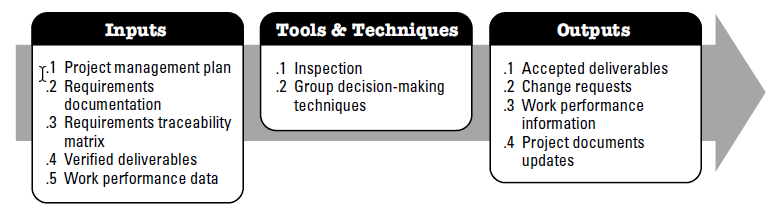
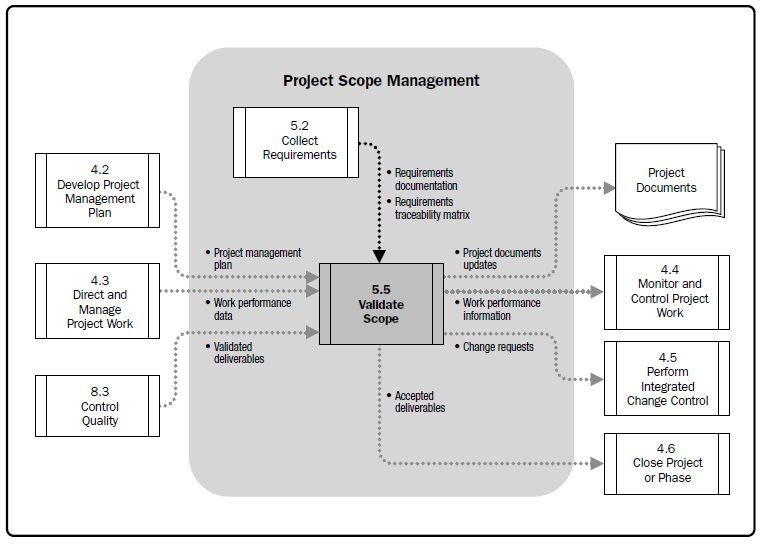
Validate Scope is the process of formalizing acceptance of the completed project deliverables. The key benefit of this process is that it brings objectivity to the acceptance process and increases the chance of final product, service, or result acceptance by validating each deliverable.
Scope Validation involves obtaining the stakeholders' formal acceptance of project deliverables. [PMBOK 5th edition, Page 133] |
| 20/07/2017 09:02:10~~~~~~manpakhong |
Project Scope Management |
Q: A management control point where scope, budget, actual cost and schedule are integrated and compared to earned value for performance measurement is called a: A. Code of accounts Answer Control accounts are placed at selected management points of the Work Breakdown Structure (WBS). Each control account may include one or more work packages, but each of the work packages must be associated with only one control account. [PMBOK 5th edition, Page 132] When doing Earned Value Management within a standard project structure there can be a defined level that is considered a "control account". A control account is normally the intersection of the functional organization doing the work and the Project organizational hierarchy. This is typically defined as the level that you can aggregate BCWS, BCWP, and Actuals AND is a level that is controlled by a single organization. Below a control account is a "Work Package". The work package is the level of the project that the user plans and a takes status on for EV. Below is the general hierarchy concept of organizing and maintaining a control account or work package:
Once the project structure is defined into control accounts and work packages responsibility and ownership can now be established. This requires assigning Control Account Managers or CAMs to play an essential role in Earned Value Management. They are responsible for the planning, coordination, and achievement of all work within a control account. They also provide authorization for all scope, technical and cost changes for their respective control accounts.
|
| 20/07/2017 08:48:48~~~~~~manpakhong |
Project Procurement Management |
Q: Unless an enterprise-wise ERP is deployed in an organization,disparate IT systems perform specialized tasks in a project. Which of the following systems typically processes supplier's payments once all the necessary certification of satisfactory work has been obtained? A. Project management information systems Answer: Payments to the seller are typically processed by the accounts payable system of the buyer after certification of satisfactory work by an authorized person on the project team. [PMBOK 5th edition, Page 383] |
| 20/07/2017 08:43:32~~~~~~manpakhong |
Project Framework |
Q: Which of these statements correctly links project and product life cycles? A. A product life cycle is generally contained within a project life cycle. Answer: The product life cycle usually consists of sequential, non-overlapping product phases. The project life cycle is typically contained within one or more product life cycles. [PMBOK 5th edition, Page 12, 13, 38] |
| 20/07/2017 08:38:01~~~~~~manpakhong |
Project Quality Management |
Q: You are looking at various process improvement models. Which of the following is not a process improvement model? A. Malcolm-Baldrige Answer: [PMBOK 5th edition, Page 220]
Malcolm-Baldrige
|
| 20/07/2017 08:08:48~~~~~~manpakhong |
Project Procurement Management |
Q: Three years back, your organization awarded a fixed price contract to a reputable local contractor to construct a new airport terminal in the city. Few days back, you have received a change request from the contractor requesting to adjust the price of the contract. The contractor is claiming that as a result of the recent national recession, the prices of raw materials have gone up and he cannot complete the rest of the project at the contract price. Is the contactor's request legitimate?
Answer Unless this is no provision for economic price adjustment due to inflation, a fixed price contract's value cannot be changed. Usually fixed price contracts spanning over one year in duration have this provision built into the contract. |
| 20/07/2017 07:28:43~~~~~~manpakhong |
Project Cost Management |
Q: Martin is the project manager of a project that is in an early phase. He needs to estimate costs but finds that he has a limited amount of detaile dinformation about the project. Which of the following estimation techniques would be least suited to his requirements? Answer: Bottom-up estimating is a technique that can be applied only when there is a sufficient amount of detail available to the project manager. [PMBOK 5th edition, Page 205] |
| 20/07/2017 07:18:53~~~~~~manpakhong |
Project Scope Management - WBS |
Q: Which of the following processes produces a work breakdown structure as an output? Answer: [PMBOK 5th edition, Page 125] |
| 20/07/2017 06:44:23~~~~~~manpakhong |
Quality Management - Quality assurance team |
You are in the middle of a major new facility construction project. The structural steel is in place and the heating conduits are going into place when a senior manager informs you that he is worried the project will not meet the quality standards. What should you do in this situation? |
| 20/07/2017 06:34:32~~~~~~manpakhong |
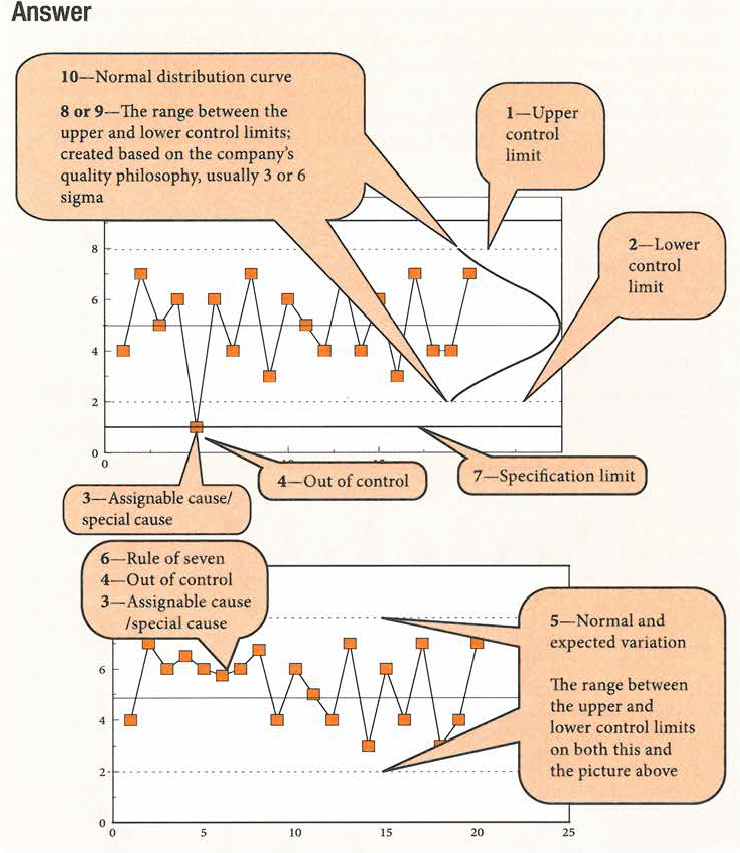
Quality Management - rule of seven |
Q: A control chart shows seven data points in a row on one side of the mean. What should be done? |
| 20/07/2017 04:40:22~~~~~~manpakhong |
Quality Management |
Q: A project has faced major difficulties in the quality of its deliverables. Management now states that quality is the most important project constraint. If another problem with quality were to occur, what would be the BEST thing for the project manager to do? Answer: If a problem with quality were to occur again, many people would opt to fix the |
| 20/07/2017 04:34:24~~~~~~manpakhong |
Quality Management - Marginal analysis |
Q: To what does the following definition refer? “The point where the benefits or revenue to be received from improving quality equals the incremental cost to achieve that quality.”
|
| 19/07/2017 04:51:47~~~~~~manpakhong |
Process Decision Program Charts (PDPC) |
Typically used in conjunction with tree diagrams, these charts let you decompose a goal into the steps required to achieve it. Each step is then reviewed for potential risk. For example, imagine that one goal of your process improvement plan is to increase the accuracy of estimates to 88 percent. Using PDPC, you can break down the steps to achieve that goal. The team might then brainstorm ideas for anything that could go wrong, and come up with contingency plans to keep things on track. The process decision program chart (PDPC) systematically identifies what might go wrong in a plan under development. Countermeasures are developed to prevent or offset those problems. By using PDPC, you can either revise the plan to avoid the problems or be ready with the best response when a problem occurs. When to Use PDPC
PDPC Procedure
Here are some questions that can be used to identify problems.
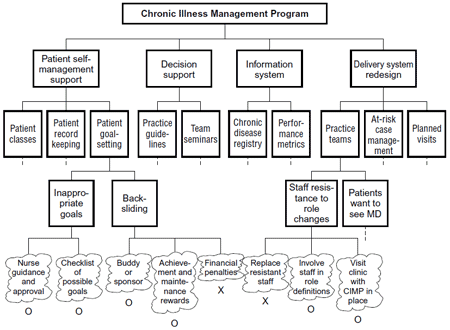
PDPC ExampleA medical group is planning to improve the care of patients with chronic illnesses such as diabetes and asthma through a new chronic illness management program (CIMP). They have defined four main elements and, for each of these elements, key components. The information is laid out in the process decision program chart below. Dotted lines represent sections of the chart that have been omitted. Only some of the potential problems and countermeasures identified by the planning team are shown on this chart.
For example, one of the possible problems with patients’ goal-setting is backsliding. The team liked the idea of each patient having a buddy or sponsor and will add that to the program design. Other areas of the chart helped them plan better rollout, such as arranging for all staff to visit a clinic with a CIMP program in place. Still other areas allowed them to plan in advance for problems, such as training the CIMP nurses how to counsel patients who choose inappropriate goals. |
| 18/07/2017 04:09:43~~~~~~manpakhong |
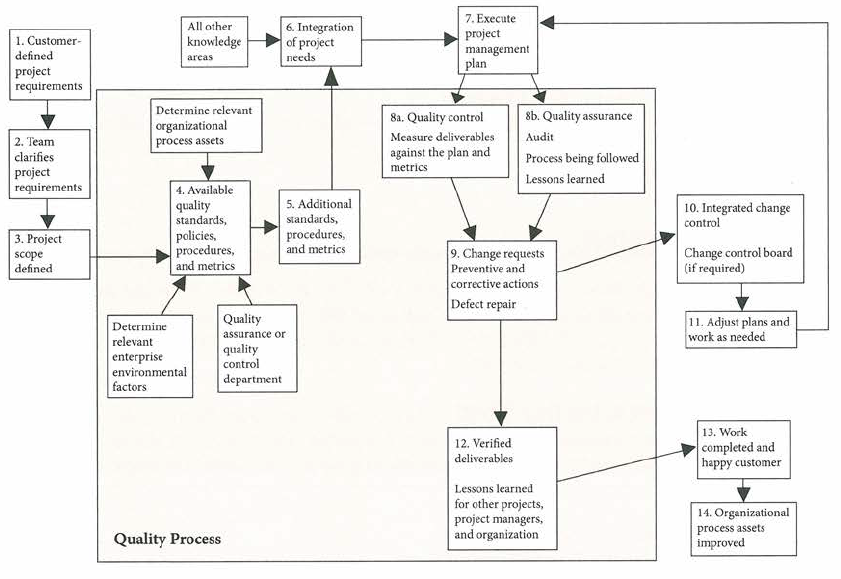
Project Quality Management |
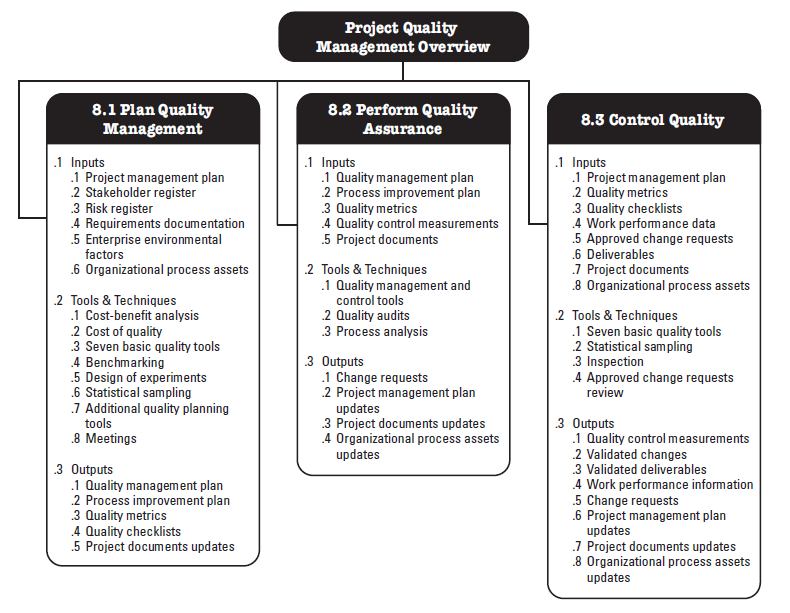
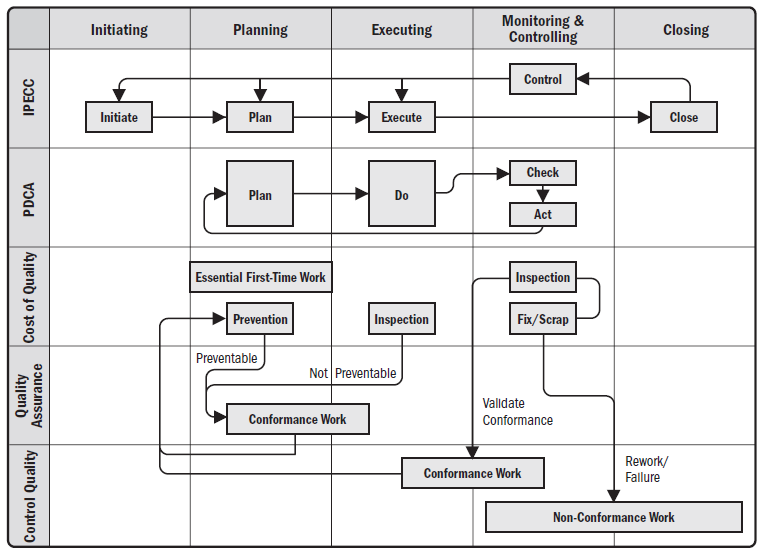
Project Quality Management Overview
Fundamental Relationships of Quality Assurance and Control Quality to the IPECC, PDCA, Cost
|
| 18/07/2017 02:58:59~~~~~~manpakhong |
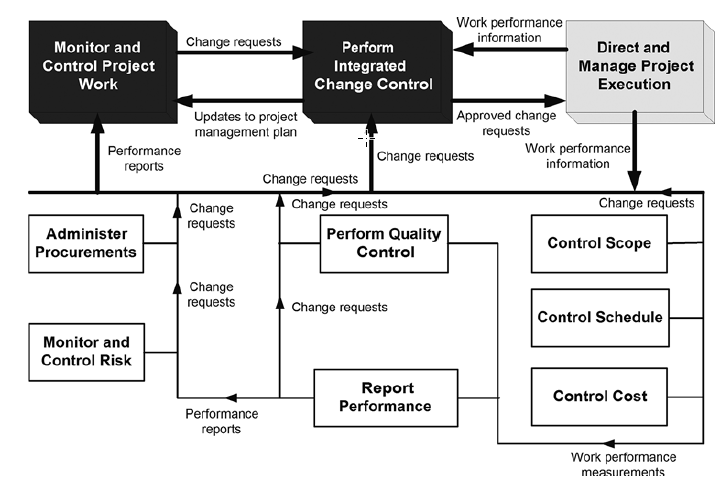
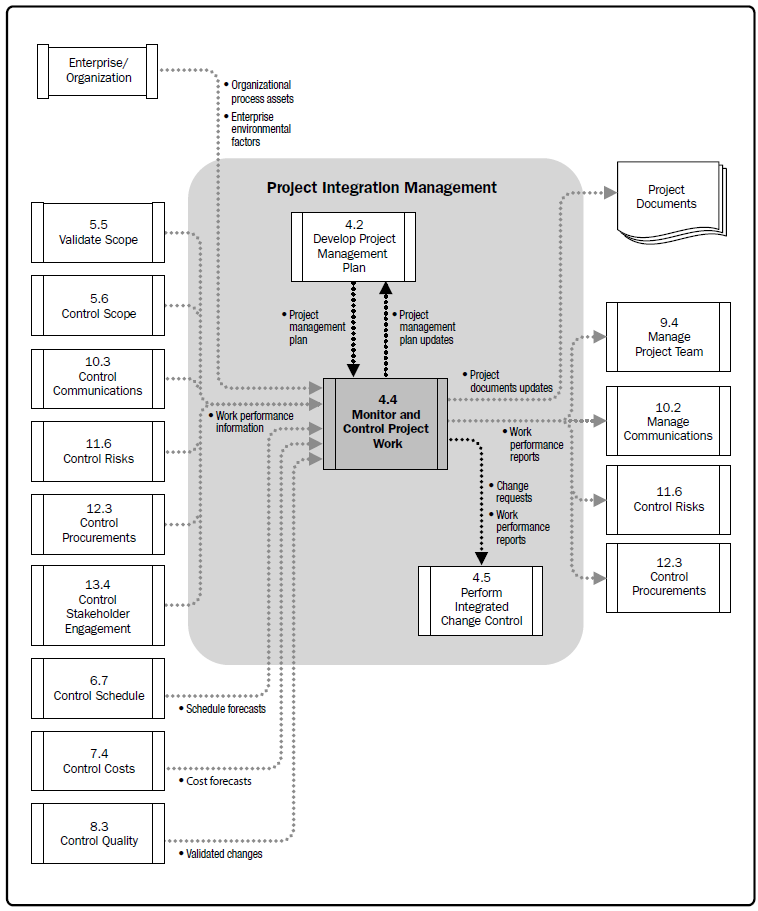
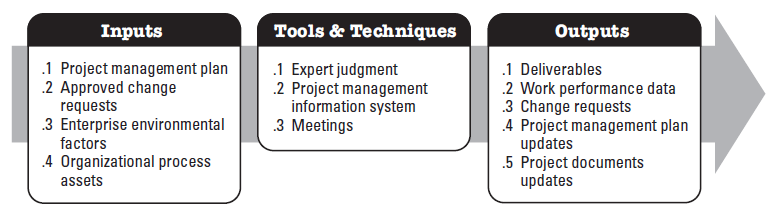
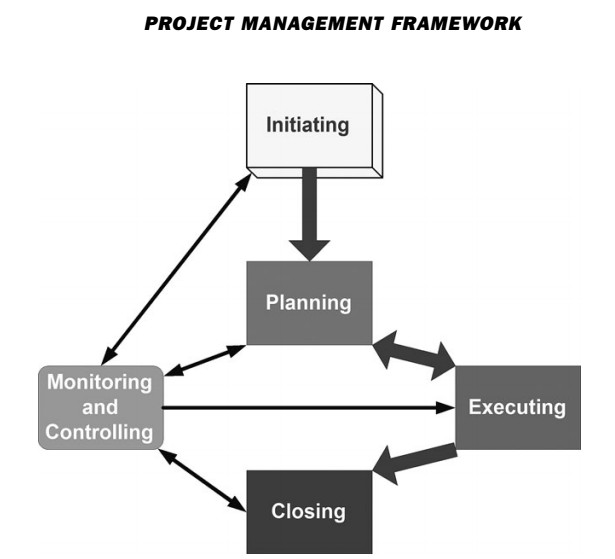
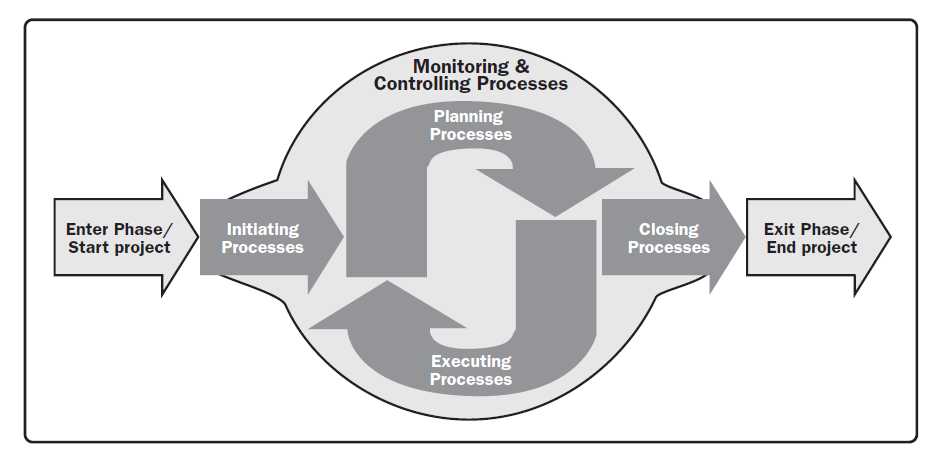
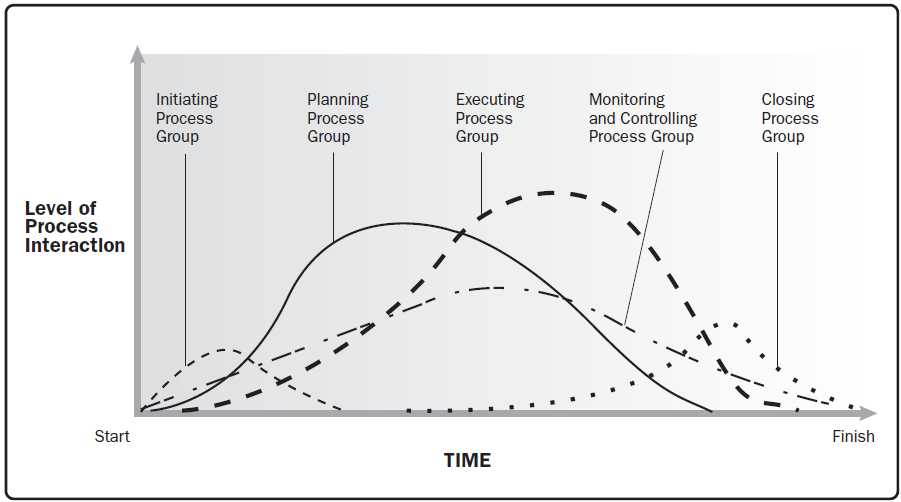
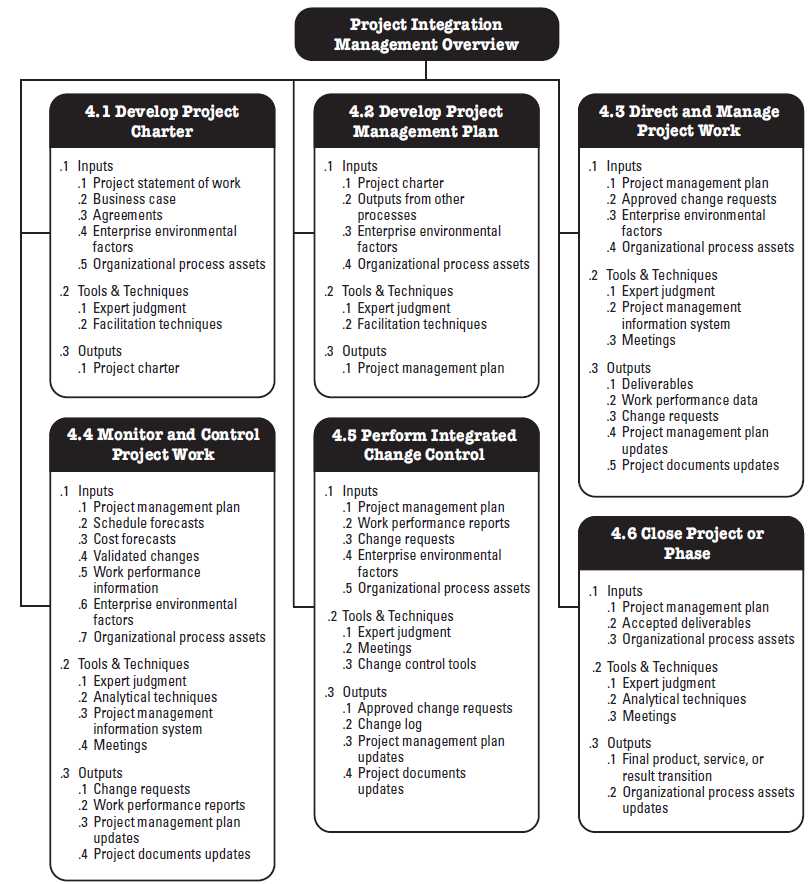
Project Integration - Monitor and Control Project Work |
Monitor and Control Project Work is the process of tracking, reviewing, and reporting the progress to meet the performance objectives defined in the project management plan. The key benefit of this process is that it allows stakeholders to understand the current state of the project, the steps taken, and budget, schedule, and scope forecasts.
Monitoring is an aspect of project management performed throughout the project. Monitoring includes collecting ,measuring, and distributing performance information, and assessing measurements and trends to effect process improvements. Continuous monitoring gives the project management team insight into the health of the project and identifies any areas that may require special attention. Control includes determining corrective or preventive actions or replanning and following up on action plans to determine whether the actions taken resolved the performance issue. The Monitor and Control Project Work process is concerned with:
|
| 18/07/2017 02:51:17~~~~~~manpakhong |
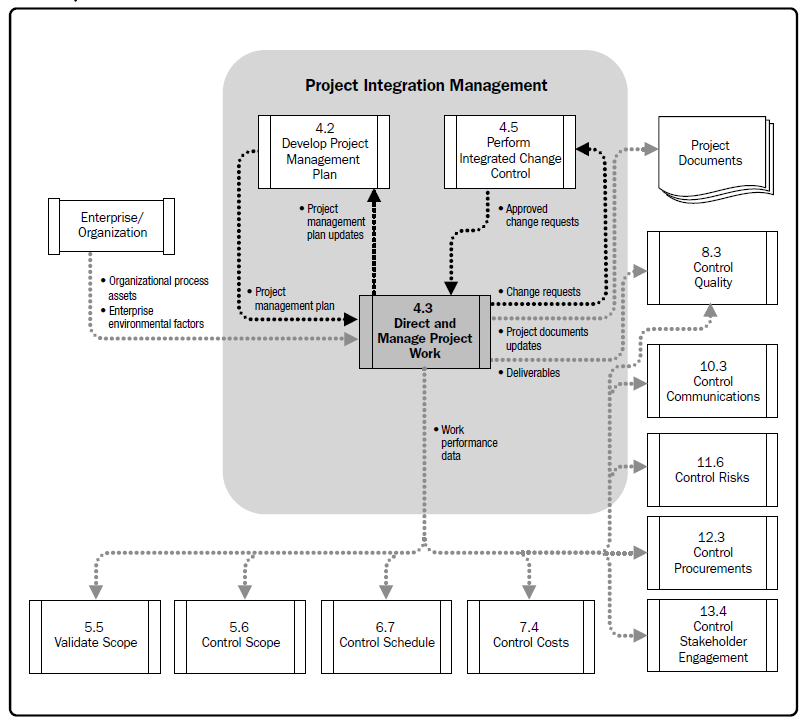
Project Integration - Direct and Manage Project Work |
Direct and Manage Project Work is the process of leading and performing the work defined in the project management plan and implementing approved changes to achieve the project’s objectives. The key benefit of this process is that it provides overall management of the project work.
Direct and Manage Project Work activities include, but are not limited to:
The project manager, along with the project management team, directs the performance of the planned project activities and manages the various technical and organizational interfaces that exist within the project. The project manager should also manage any unplanned activities and determine the appropriate course of action. The Direct and Manage Project Work process is directly affected by the project application area. Deliverables are produced as outputs from processes performed to accomplish the project work as planned and scheduled in the project management plan. During project execution, the work performance data is collected and appropriately actioned and communicated. Work performance data includes information about the completion status of deliverables and other relevant details about project performance. The work performance data will also be used as an input to the Monitoring and Controlling Process Group. Direct and Manage Project Work also requires review of the impact of all project changes and the implementation of approved changes:
|
| 18/07/2017 02:06:43~~~~~~manpakhong |
Project Integration Management |
The Monitor and Control Project Work process is responsible for keeping track of the project's measures, including cost. The Monitor and Control Project Work process monitors the project performance while the Direct and manage Project Work process is concerned with performing the activities to accomplish project requirements. The Monitor and Control Project Work process monitors the other project processes including the Direct and Manage Project Work process, while the Direct and Manage Project Work Process completes the project scope.
A. Throughout the entire project
Integrated Change Control process is valuable for managing and tracking those changes. Q: Which of the following is not an output of the Direct and Manage Project Work process? A. Deliverables
The Direct and Manage Project Work process has several outputs, including deliverables, work performance data, change requests, project management plan updates and project document updates. The project management plan is an input to the process. |
| 17/07/2017 08:30:02~~~~~~manpakhong |
Knowledge Area: Project Management Framework |
Q. Which of the following is an input to the Develop Project Team process? A. Resource Requirements Answer: Q. Which of the following is an enterprise environmental factor? A. Configuration management knowledge base Answer:
|
| 12/07/2017 02:26:24~~~~~~manpakhong |
Scope Management - a series of questions and answers |
Q: The work breakdown structure can BEST be thought of as an effective aid for communications. Answer: The term “stakeholder” encompasses all the other choices. In this case, it is the best answer since the WBS can be used (but does not need to be used) as a communications tool for all stakeholders to “see” what is included in the project.
Answer: The Validate Scope process occurs during project monitoring and controlling. It is done at the end of each project phase to get approval for phase deliverables, as well as at other points to get approval for interim deliverables. Q: The project is mostly complete. The project has a schedule variance of 300 and a cost variance of —900. All but one of the quality control inspections have been completed and all have met the quality requirements. All items in the issue log have been resolved. Many of the resources have been released. The sponsor is about to call a meeting to obtain product validation when the customer notifies the project manager that they want to make a major change to the scope. The project manager should: Answer: Do not jump into the problem without thinking. The customer only notified the project manager that they want to make a change. They did not describe the change. The project manager should not say no until he or she knows more about the potential change, nor should the project manager go to management without more information. The project manager must understand the nature of the change and have time to evaluate the impact of that change before doing anything else. Of these choices, the first thing to do is to determine what the change is. The project manager might then analyze the potential change with the team, but only if their input is required.
Answer:
Q: The MAIN purpose of writing a user story is: A user story is a way of stating a requirement, often using the following format: As a <Role>, I want <Functionality/Goal>, so that <Business Benefit/Motivation>. User stories may be developed in facilitated workshops or as part of other requirements-gathering methods.
Q: You are managing a six-month project and have held bi-weekly meetings with your project stakeholders. After five-and-a-half months of work, the project is on schedule and budget, but the stakeholders are not satisfied with the deliverables. This situation will delay the project completion by one month. The MOST important process that could have prevented this situation is: Answer: Monitor and Control Risks, Control Schedule, and Control Scope are monitoring and controlling processes. This situation asks how to prevent the problem, which would have been done during planning. The project deliverables are defined in the Define Scope process, which is a part of project planning. Good planning reduces the likelihood of a situation like the one described, by including the right people and spending adequate time clarifying the project scope. The development of the scope baseline can BEST be described as involving: Answer: Q: After obtaining input from the customer and other stakeholders, the project team is responsible for developing the scope baseline. Remember that the scope baseline includes the WBS, WBS dictionary, and project scope statement. Which of the following can create the MOST misinterpretation of the project scope statement? Answer: Much of the work on the project is dictated by the project scope statement. Any imprecision in such a key document will lead to differing interpretations. |
| 11/07/2017 08:06:59~~~~~~manpakhong |
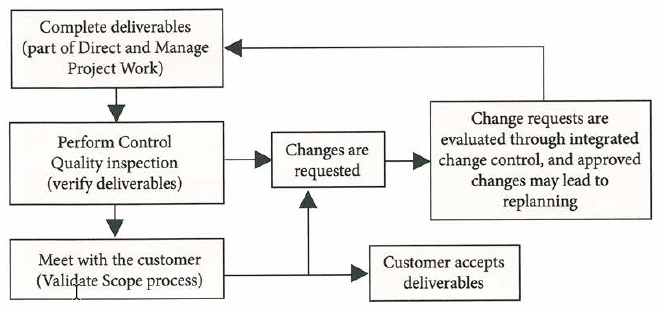
Relationship between Verify Scope and Control Quality |
|
| 11/07/2017 07:51:52~~~~~~manpakhong |
Validated scope |
The validate scope process: frequent, planned meetings with the customer or sponsor to gain formal aceptance of deliverables during project monitoring and controlling.
|
| 11/07/2017 07:47:42~~~~~~manpakhong |
Scope baseline |
For scope, the baseline is the version of the:
|
| 11/07/2017 06:46:03~~~~~~manpakhong |
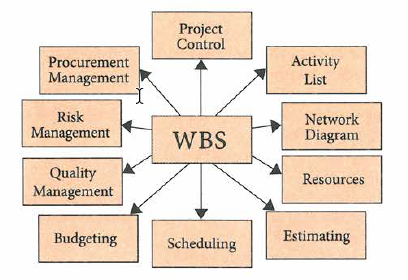
WBS - foundation of the project |
|
| 11/07/2017 06:30:10~~~~~~manpakhong |
Work packages |
Work packages are reached when deliverables:
|
| 11/07/2017 06:23:55~~~~~~manpakhong |
How to create WBS? |
|
| 10/07/2017 09:21:01~~~~~~manpakhong |
Project Integration Management - Manage Communication |
Q: Julia is currently recruiting her project team. She has carried out various interviews and has shortlisted potential candidates. Now, according to the project communication management plan, she has to submit the shortlisted profiles to the project client (customer of the project) for approval. Only the approved candidates can then be formally hired for the project. The submission of the profiles to the client will be done through which of the following processes? Answer: Manage Communications is the process of distributing project information in accordance to the communications management plan. The interviews and shortlisting was carried out during the Qcquire Project Team and so will be the hiring once the approvals come in. However, the profiles submission to the client will be done through the Manage Communications process. |
| 10/07/2017 09:14:34~~~~~~manpakhong |
Project Integration Management - Sunk cost |
Sunk cost is defined as a cost that has already been incurred and which cannot be recovered. [PMI best practice; not explicitly stated in PMBOK] |
| 10/07/2017 08:52:58~~~~~~manpakhong |
Project Human Resource Management - Colocation |
Colocation is a tool and technique of the Develop Project Team process. The term co-location represents an organizational technique in which the location of team members is determined in a strategic way to maximize productivity. The specific ways in which this is done is varied, but essentially as follows. When co-location is practiced at the start o a project (or, for that matter, it can be enacted at any time), the project team members are moved to alternate locations (either full-time or only for parts of days) to allow them to better work with one another, and on the project in general. This is because typically this newer organizational placement is done in a way which provides for improved communication among the team members, the ability to form better and closer working relationships, and in many cases can lead to improved productivity (for the reasons above as well as for other more materials ones, such as better access to sophisticated office equipment). |
| 10/07/2017 08:40:23~~~~~~manpakhong |
Project Communications Management - Communications channel formula |
The communications channel formula is: ch = n * (n-1) /2
|
| 10/07/2017 08:32:37~~~~~~manpakhong |
Project Scope Management - ideas generation tools |
Q: Which of the following is not a general management technique used to generate different approaches to execute and perform the project work? Answer: Alternatives Identification concerns itself with identifying techniques to generate different approaches to execute and perform the work of the project. Map-Out is not a valid technique; the other three (brainstorming, lateral thinking and analysis of alternatives) are techniques use4d to generate ideas for different approaches. |
| 10/07/2017 08:10:35~~~~~~manpakhong |
Project Framework - Progressive elaboration vs Scope creep |
Q: Which of the following is incorrectly represented by the term Progressive Elaboration? Answer: The distinction between progressive elaboration and scope creep needs to be understood since the two terms are different. The changes to scope (especially in an uncontrolled manner) are called scope creep. In contrast, progressive elaboration involves building on or elaborating the output of a previous phase. |
| 10/07/2017 07:35:10~~~~~~manpakhong |
Project Quality Management - Pareto chart (Pareto distribution diagram) |
A Pareto chart, also called a Pareto distribution diagram, is a vertical bar graph in which values are plotted in decreasing order of relative frequency from left to right. Pareto charts are extremely useful for analyzing what problems need attention first because the taller bars on the chart, which represent frequency, clearly illustrate which variables have the greatest cumulative effect on a given system. A Pareto chart can be used to quickly identify what business issues need attention. By using hard data instead of intuition, there can be no question about what problems are influencing the outcome most.
|
| 10/07/2017 07:26:16~~~~~~manpakhong |
Project Time Management - Schedule estimation |
Q: If you are working on a project where there is no definite detailed scope, but similar projects have completed in the past, what is the correct Estimate Activity Durations tool to use? a. Three Point Estimating
Analogous, parametric, and three-point estimating techniques are all accepted practices for determining the correct amount of time required for a portion of the project. The Critical Path Analysis techniques evaluate the whole project schedule. |
| 10/07/2017 07:17:20~~~~~~manpakhong |
Project Risk Management - Quantitative risk analysis |
Q: Quantitative risk analysis should be performed: Answer: Since the quantitative risk analysis is a more in-depth process, it should only beperformed on prioritized risks to minize impact to the overall project schedule. [PMBOK 5th edition, Page 334] |
| 10/07/2017 07:13:21~~~~~~manpakhong |
Project Cost Management - The schedule variance |
The schedule variance is the earned value minus the planned value. schedule variance = earned value - planned value At the end of the project, all of the planned values should be earned, and the differences should be zero. |
| 10/07/2017 06:57:25~~~~~~manpakhong |
Project Quality Management - 7 basic tools of quality control |
Seven basic tools of quality control:
|
| 10/07/2017 06:51:13~~~~~~manpakhong |
Project Time Management - Fast tracking vs Crashing |
Fast tracking
It is usually important to start with this technique first. The main reason for this is that fast tracking does not involve any costs. It is simply a rearrangement of the activities in the original schedule. Although fast tracking may not result in an increase in the cost, it leads to an increase in the risk, because activities that were originally intended to be performed sequentially are now performed in parallel. It may lead to a rework or rearrangement of the project. This reworking of the project can cause loss of even more time. It should be noted, however, that fast-tracking can only be applied if the activities in question can actually be overlapped. In conclusion, the person managing the project, in order to know whether it is going to be worthwhile, must weigh the pros and cons of fast tracking against each other. A person must decide whether he or she is willing to make the trade-off between having this increased risk for a cost, and being able to implement a shorter project schedule.
Crashing
Crashing is expensive because we are adding more resources to the project. Undoubtedly, if you add more resources to an activity or project, it is going to cost you more. It only works for critical path activities where it is possible to shorten schedules. Crashing analyzes and categorizes activities based on the lowest crash cost per unit time, allowing the team behind the project to identify those activities that will be able to deliver the most value at the least incremental cost. The results of a crashing analysis are usually in a crash graph, and activities with the flattest slope are the ones that will be considered first, for the simple reason that they lead to an equal amount of time savings, but have a smaller increase in cost. When the crashing approach is used, any additional costs associated with rushing the project are reviewed against the possible benefits of completing the project within a shorter span of time. In addition to that, other items that are considered when one is using the crashing approach include adding more resources to the project, allowing additional overtime, paying extra to receive delivery of critical components more quickly, among others. Crashing only works if the additional resources are going to allow you to complete the project sooner. If the fast tracking did not accelerate the schedule enough, the team behind the project is going to consider adding resources to the critical activities of the project. The manager of the project should take into consideration those resources that have the lowest associated costs and start with the lowest incremental cost resource pool first. |
| 10/07/2017 04:47:44~~~~~~manpakhong |
Project communications Management - Project Communications Management |
Q:James is managing a shopping mall construction project. During the project execution he finds out that the project communications management plan is not effective and requires a major update. Which of the following processes will issue a change request for the required update? a. Plan Communications Management Answer: Control Communications Change request is an output of the Control Communications process. The Control Change process will produce the change request, the Perform Integrate Change Control process will get that approved, and then the Plan Communications process will make the necessary updates. [PMBOK 5th edition, Page 307] PMBOK 10.3.3.3 Project Management Plan Updates |
| 10/07/2017 03:47:10~~~~~~manpakhong |
Project Time Management - Rolling Wave Planning |
Q: When would Rolling Wave Planning be useful in a project? a. You should use Rolling Wave Planning to help you achieve the appropriate level of detail in each work package at the right time. Answer: You should use Rolling Wave Planning to help you achieve the appropriate level of detail in each work package at the right time. Rolling Wave Planning is a technique used to create a more detailed work plan while keeping the right level of detail for each activity: Activities happening sonner have more detail than those further in the future. [PMBOK 5th edition, Page 152] |
| 10/07/2017 03:37:57~~~~~~manpakhong |
Project Integration Management - Identify key deliverables |
The best position for the process "Identify Key Deliverables" process. a. Define Scope and Create WBS Answer: Collect Requirements and Define Scope The identification of key project deliverables can only be done once the project requirements are collected, analyzed and documented. This is done during the Collect Requirements process. Further, the key project deliverables are documented in the project scope statement which is an output of the Define Scope process. The best position of the newly proposed "Identify Key Deliverables" process should be between the Collect Requirement and Define Scope processes. [PMBOK 5th edition, Pages 110, 120] |
| 10/07/2017 03:26:37~~~~~~manpakhong |
Precedence Diagramming Methods |
Precedence Diagramming Methods:
Not commonly used - Start to Finish relationships indicate that the next task cannot be completed until the one preceding it has started. This type is not commonly used.[PMBOK 5th edition, Page 157] Most commonly used - A-Finish-to-Start relationships indicate that the next task is not able to start until the one preceding it is completed. This is the most commonly used type of activity relationship. [PMBOK 5th edition, Page 157] |
| 10/07/2017 02:58:21~~~~~~manpakhong |
Project Scope Management - Requirements Traceability Matrix |
Requirements Traceability Matrix is an output of the Collect Requirements process. It is used for tracing requirements to project scope, objectives, and test strategy. Tracing requirements to project risk is not a valid use. [PMBOK 5th edition, Pages 117, 118] What is Traceability Matrix? A traceability matrix is a document that co-relates any two-baseline documents that require a many-to-many relationship to check the completeness of the relationship. It is used to track the requirements and to check the current project requirements are met. What is Requirement Traceability Matrix (RTM)? Requirement Traceability matrix or RTM captures all requirements proposed by the client or development team and their traceability in a single document delivered at the conclusion of the life-cycle. In other words, it is a document that maps and traces user requirement with test cases. The main purpose of Requirement Traceability Matrix is to see that all test cases are covered so that no functionality should miss while testing. Requirement Traceability Matrix - Parameters include
On the basis of Business Requirement Document (BRD), Technical Requirement Document (TRD) and unit test document. Business Requirement Document (BRD):
Technical Requirement Document (TRD):
Unit test cases:
Mapping TR with Test case:
Mapping Br, Tr and unit test
Requirement Traceability Test Matrix:
Sample of RTM from PMBOK:
|
| 10/07/2017 01:49:30~~~~~~manpakhong |
Project Quality Management |
Q: Which of the following tools and technique used during the Control Quality process? Answer: Supplier|Input|Process|Output|Customer
The SIPOC tool is particularly useful when it is not clear:
Salience Model Salience Model categories stakeholders according to their prominence by ranking stakeholders according to their power, legitimacy and urgency. Power: to influence the project deliverables or the organization Legitimacy: of their interaction with the project and it's appropriateness Urgency: of their communication requirements
|
| 07/07/2017 08:37:28~~~~~~manpakhong |
Project Framework - Phase Gate Process |
Project Framework Phase–gate process Project management technique in which an initiative or project (e.g., new product development, process improvement, business change) is divided into stages (or phases) separated by gates. At each gate, the continuation of the process is decided by (typically) a manager or a steering committee. The decision is based on the information available at the time, including the business case, risk analysis, and availability of necessary resources (e.g., money, people with correct competencies) These points are referred to as Phase exits, |
| 06/07/2017 03:27:59~~~~~~manpakhong |
Information Gathering Techniques |
Brainstorming - The goal of brainstorming is to obtain a comprehensive list of project risks. The project team usually performs brainstorming, often with a multidisciplinary set of experts who are not part of the team. Ideas about project risk are generated under the leadership of a facilitator, either in a traditional free-form brainstorm session or structured mass interviewing techniques. Categories of risk, such as in a risk breakdown structure, can be used as a framework. Risks are then identified and categorized by type
Interviewing - Interviewing experienced project participants, stakeholders, and subject matter experts helps to identify risks. Root cause analysis -Root-cause analysis is a specific technique used to identify a problem, discover the underlying causes that lead to it, and develop preventive action. |
| 06/07/2017 03:15:24~~~~~~manpakhong |
Project Communications Management - Communication Models |
Communication Models
|
| 06/07/2017 02:33:06~~~~~~manpakhong |
Project Management Framework |
|
| 05/07/2017 09:10:45~~~~~~manpakhong |
Project Communications Management - CPI |
Q. A contractor is currently constructing a new building for your organization on a cost-plus-incentive contract. You have just received the project status report from the contractor's project manager. According to the report, the project's CPI is 1.5. You are shocked as you believe that the project costs are out of control. Upon investigation you find out that the $1 million advane payment (20% of the estimated project cost) to the contractor at the start of the project has been included in the earned value of the project. Further the cost of the inventory at the project site has been excluded from the total actual costs. According to the contract, your company only reimburses the costs for the completed deliverables and not for the supplies in the project's inventory. In this scenario, the reported project's CPI is incorrect because: Answer: In this scenario the earned value has been overstated while the reported actual cost is ok. Earned value should be the sum of PVs of all completed activities. The initial 20% advance should not be part of this. Further, since the buyer is not liable for the inventory cost and only reimburses the costs associated with completed deliverables, the cost of the inventory does not become part of the actual cost until that inventory is consumed during the construction process. The inventory is an asset for the contractor until it is consumed on the project and at that time it becomes a cost for the project. |
| 05/07/2017 08:53:17~~~~~~manpakhong |
The cost variance (CV) |
If the project's current total earned value (EV) is $100,000 and the actual amount spent (AC) is $95,000, what is the cost variance of the project? The cost variance (CV) = total earned value (EV) - the acutual amount spent (AC). |
| 05/07/2017 08:47:42~~~~~~manpakhong |
RACI |
Responsible, Accountable, Consult and Inform statuses:
|
| 05/07/2017 08:29:13~~~~~~manpakhong |
Initialization - Net Present Value |
Net Present Value Answer: 2485884 Present Value = Future Value / (1 + rate)^period x * (1 + 0.15)^5 = 5000000
|
| 05/07/2017 07:32:15~~~~~~manpakhong |
Project Scope Statement |
Q: Project requirements are determined during the Collect Requirements process through various toos and techniques. These requirements form the basis for defining the project scope. One of the responsibilities of a project manager is to identify key project deliverables during this exercise. Where are the key project deliverables documented? Answer: Project Scope Statement Project Scope Statement - The primary result, or output, of the Define Scope process is the project scope statement. This document in effect says “Here is what we will do on this project” or “Here is the approved project and product scope for this project.” The development of the project scope statement can take a lot of time and involve the expert judgment of many stakeholders and even experts from outside the organization. While defining requirements and, in turn, defining scope, you should identify areas where people requested scope but it was not approved to be included in the project. You should also clarify areas where the scope could easily be misunderstood. It is a waste of project time and money to create scope that is not needed or approved, yet it is easy for this to occur. One way to avoid this problem is to identify in the project scope statement what is not in the project to make it clear that such additions are not allowed.
The project scope statement may include:
|
| 05/07/2017 06:49:32~~~~~~manpakhong |
Project Procurement Management |
Q. During the Control Procurements process, a number of documents might get updated due to varous reasons. Which of the following components of the project management plan is least likely to get updated during this process? Answer: |
| 05/07/2017 06:04:17~~~~~~manpakhong |
Project Cost Management - Contingency funds |
Contingency funds are used to handle cost uncertainty due to unforeseen purchases that may be needed during a project. These funds are generally used for items that are likely to occur but are not certain to occur. Activity cost estimates are quantitative assessments of the probable costs required to complete project work. Cost estimates can be presented in summary form or in detail. Costs are estimated for all resources that are applied to the activity cost estimate. This includes, but is not limited to, direct labor, materials, equipment, services, facilities, information technology, and special categories such as cost of financing (including interest charges), an inflation allowance, exchange rates, or a cost contingency reserve. Indirect costs, if they are included in the project estimate, can be included at the activity level or at higher levels. |
| 05/07/2017 04:16:43~~~~~~manpakhong |
Project Framework - Composite organization |
Q. A fundamentally functional organization creates a special project team to handle a critical project. This team has many of the characteristics of a project team in a project organization and has a Project Manager dedicated to the project. Such an organization is called: a. A projectized organization b. A functional organization c. A strong matrix organization d. A composite organization Answer: A composite organization [PMBOK 5th edition, Page 25] |
| 05/07/2017 04:16:42~~~~~~manpakhong |
Project Framework - Composite organization |
Q. A fundamentally functional organization creates a special project team to handle a critical project. This team has many of the characteristics of a project team in a project organization and has a Project Manager dedicated to the project. Such an organization is called: a. A projectized organization b. A functional organization c. A strong matrix organization d. A composite organization Answer: A composite organization [PMBOK 5th edition, Page 25] |
| 05/07/2017 04:00:30~~~~~~manpakhong |
Project Integration Management - Tricky Question - Stakeholders |
Q: During which of the following processes project key stakeholders get engaged with the project for the first time? a. Develop Project Charter b. Identify Stakeholders c. Collect Requirements d. Plan Stakeholder Management Answer: Develop Project Charter Project stakeholders are involved in each of the project management processes. The Develop Project Charter is the first project management process where the key project stakeholders get engaged for the first time. Stakeholders provide expert judgment and participate in facilitated sessions during the charter development. [PMBOK 5th edition. Page 71] [Project Integration Management] |
| 05/07/2017 01:33:43~~~~~~manpakhong |
10 knowledges area & 5 process groups |
10 knowledges area
5 process groups
|
| 04/07/2017 22:21:25~~~~~~manpakhong |
Initiating - Benefit Cost Ratio |
Benefit Cost Ratio ( BCR ) = Revenue/ Cost . The Benefit-Cost Ratio (BCR), or profitability index, is a commonly used project management tool often used to identify the most efficient projects. The BCR is derived from the mathematics of Net Present Value (NPV), which was designed to model situations where a substantial initial investment is followed by an ongoing revenue stream. NPV relies on the assumptions of the discounting model, which are not always valid for technology projects. IT projects tend to have a short duration, complex interdependencies, and high uncertainty, and the BCR is inaccurate when used with interdependent or mutually exclusive projects. Although BCR can be a useful tool, it has inherent measurement difficulties when used for selecting projects; the degree of alignment with business strategy is a better criterion.
|
| 04/07/2017 21:47:05~~~~~~manpakhong |
Human Resource Management - Herzberg s Theory |
Q. Responsibility, self-actualization, professional growth, and recognition are motivatingagents according to which motivational theory?
Answer: Herzberg's theory - responsibility, self-actualization, professional growth, and recognition are motivating agents according to herzbergs theory. Herzbergs theory deals with hygiene factors and motivating agents. Hygiene factors include working conditions, salary, personal life, relationships at work, security and status. Motivating agents are responsibility, self actualization, professional growth and recognition. Theory x is one of the theories put forth by Mcgregor in which he classified all workers into two groups, x and y. According to theory x, workers will not work unless made to work by the supervisor. They would need close monitoring as they avoid responsibility. According to theory y, workers are always willing to work. They would not need supervision, and they direct their own effort towards achieving the tasks specified. Maslow established the theory of a hierarchy of needs. In his theory, Maslow stated that human beings are motivated by unsatisfied needs, and that certain lower needs need to be satisfied before higher needs can be satisfied. According to this theory, Maslow identified the following needs, in order of their levels, from lowest to highest: |
| 04/07/2017 21:34:30~~~~~~manpakhong |
Closing - dispute |
Q: You are involved in the Close Procurements process. The seller disagrees with you over several issues. a. mediation Answer: Meditation is a special type of negotiation whereby a third party is used as the negotiator of the settlement. However, the findings of the third party are not binding. Negotiation generally occurrs between the two parties. Both parties discuss the issues and reach an agreement on the result. Auditing occurs when a procurement is reviewed to identify the successes and failures of the Project Procurement Management knowledge area. |
| 04/07/2017 19:54:40~~~~~~manpakhong |
Planning - the inputs to the Collect Requirements (PMBOK 5th Edition) |
the inputs to the Collect Requirements:
|
| 04/07/2017 19:45:16~~~~~~manpakhong |
Initiating - Definition of a Project |
Q: David has taken an initiative to conduct Six Sigma training for the employees of the organization to increase their productivity with few defects. He decides to conduct this training from the 15th to the 20th of April. Should this initiative be considered as a project? if so, what will be the key deliverable of this project? a. Yes, this initiative can be considered as a project. The key deliverables of this project will be improved employee skills and increased performance with fewer Answer: Any initiative that has a definite beginning and end and produces a product, service, or result can be considered as a project. Further, the deliverables of a project need not always be a product. Deliverables can also be an improvement in the existing services or product. The key deliverables of this project will be improved employee skills and increased performance with fewer defects. The initiative has a definite start and end and will produce results in the form of improved imployee skills. Therefore, it can definitely be considered as a project. The specified initiative has a definite start and end; therefore, it cannot be an operation as an operation is an ongoing process. |
| 14/05/2017 15:36:12~~~~~~manpakhong |
Initiating - Cost |
Costs are Typically higher toward the end of a project. Costs fluctuate over the course of the project life cycle. However, for the majority of project life cycles, costs typically are lower at the beginning of the project, higher toward the end of the project, and drop dramatically as the project is concluded.
|
| 04/04/2017 16:06:01~~~~~~manpakhong |
The relationship between knowledge areas and process groups |
|
| 04/04/2017 15:50:29~~~~~~manpakhong |
Project Management Process Groups Chart |
Project Management Process Groups Chart
|
| 04/04/2017 12:24:11~~~~~~manpakhong |
Project Management Process Groups |
Initiating Process Group - Those processes performed to define a new project or a new phase of an existing project by obtaining authorization to start the project or phase. Planning Prcess Group - Those processes required to establish the scope of the project, refine the objectives and define the course of action required to attain the objectives that the project was undertaken to achieve. Executing Process Group - Those processes performed to complete the work defined in the project management plan to satisfy the project specifications. Monitoring and Controlling Process Group - Those processes required to track, review, and regulate the progress and performance of the project; identify any areas in which changes to the plan are required; and initiate the corresponing changes. Closing Process Group - Those process performed to finalize all activities across all Process Groups to formally close the project or phase.
Process Groups Interact in a Phase or Project |
| 20/03/2017 15:21:37~~~~~~manpakhong |
The Cost Management Process - Inputs to Estimating Costs |
|
| 20/03/2017 15:06:30~~~~~~manpakhong | ||||||||||
The Cost Management Process | ||||||||||
|
| 20/03/2017 14:39:27~~~~~~manpakhong |
Planning - Plan Cost Management (Two techniques) |
The Plan Cost Management - to answer two questions:
Two techniques:
|
| 20/03/2017 14:36:19~~~~~~manpakhong |
Planning - Plan Cost Managment |
Q: You are producing a document that includes the cost control variance thresholds, units of measure, and level of accuracy. Which document are you creating?
Answer is: cost management plan The cost management plan is the document that includes the cost control variance thresholds, units of measure, and level of accuracy. It is created during the Plan Cost Management process. None of the other options include this information. Work performance information is created in the Control Costs process and includes the calculated cost variance, schedule variance, cost performance index, schedule performance index, and other work performance calculations. The cost baseline is created in the Determine Budget process and includes the approved budget. The activity cost estimates are created in the Estimate Costs process and include all estimated costs for the project. Rita's PMP Exam Prep: The cost management plan may include:
|
| 20/03/2017 14:11:44~~~~~~manpakhong |
Rita's Process Chart |
|
| 19/03/2017 15:26:33~~~~~~manpakhong |
Closing |
The Close Procurements process is part of the Closing Process Group. Agreement Closure is not a process. The Contract Closure process was listed in the PMBOK 3rd Edition as part of the Closing process group. HOwever, This process has been renamed the Close Procurements process in the PMBOK 4th and 5th Edition. Q: You are involved in the Close Procurements process. The seller disagrees with you over several issues. According to the agreement, a third party will be used to settle the dispute. The findings of the third party are binding. The type of proceeding you will be using is arbitration.
|
| 19/03/2017 15:23:33~~~~~~manpakhong |
Project Integration Management |
Project Integration Management Overview
|
| 19/03/2017 14:55:52~~~~~~manpakhong |
Executing |
As a project manager, you are NOT responsible for maintaining strong personal relations with the customer to be protected if anything goes wrong in the project. Seeking personal favors from the customer at the cost of the project is unethical. The first and foremost responsibility of a project manager is to protect the interests of the project and the customer. It is highly irresponsible to protect your interests instead of the project It is your responsibility as project manager to provide correct and acurate data in all esimates, protect the interests of the customer in the project, or ensure that your vendors sign the non-disclosure agreement if outsourcing the project work requires sharing confidential information with customer's approval. |
| 14/03/2017 06:46:52~~~~~~manpakhong |
Integration Management |
The customer wants to make a change to the project scope. The first action is to evaluate the impact of a change.
Due to corporate restructuring, the project sponsor, a major stakeholder, and the CEO have left the company. The project manager's project is past the halfway point and the remaining members of the management team have been lukewarm toward the project. The new CEO does not place a high value on project management methodology, and the project team is nervous about its future. Under these circumstances, the project manager's primary responsibility is to:
Providing accurate and truthful reports are always part of a project manager's professional and social responsibility. However, completing the project in a professional manner is the primary responsibility. |